Nedocromil sodium inhibits histamine-induced itch and flare in human skin
- PMID: 11159712
- PMCID: PMC1572599
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703852
Nedocromil sodium inhibits histamine-induced itch and flare in human skin
Abstract
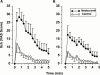
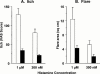
This study was designed to test the hypothesis that nedocromil sodium inhibits sensory nerve function to reduce flare and itch in human skin. Nedocromil sodium (2%) or water (control) was introduced into the volar forearm skin of eight non-atopic volunteers by iontophoresis (8 mC) and histamine (20 microl of 1 microM and 300 nM) injected intradermally 10 min later at the same site. Itch was assessed on a visual analogue scale every 20 s for 5 min. Weal and flare areas and mean blood flux within the flare were assessed by scanning laser Doppler imaging at 10 min. The results showed that nedocromil sodium reduced itch scores, totalled over 5 min, by approximately 74.0% (P<0.005) and flare areas by approximately 65% (P<0.03). Neither weal areas nor blood flux within were reduced. These data demonstrate that nedocromil sodium is effective in reducing neurogenic itch and flare in the skin. We suggest that its mechanism of action is modulation of sensory neurone activation or conduction in the skin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Investigation into the mechanisms by which nedocromil sodium, frusemide and bumetanide inhibit the histamine-induced itch and flare response in human skin in vivo.Clin Exp Allergy. 2004 Mar;34(3):450-5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.01898.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004. PMID: 15005740 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the effects of desloratadine and levocetirizine on histamine-induced wheal, flare and itch in human skin.Inflamm Res. 2003 Oct;52(10):424-7. doi: 10.1007/s00011-003-1193-5. Inflamm Res. 2003. PMID: 14520518 Clinical Trial.
-
Botulinum toxin type A reduces histamine-induced itch and vasomotor responses in human skin.Br J Dermatol. 2009 Oct;161(4):737-45. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2009.09305.x. Epub 2009 May 11. Br J Dermatol. 2009. PMID: 19624547 Clinical Trial.
-
Connections between Immune-Derived Mediators and Sensory Nerves for Itch Sensation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 16;22(22):12365. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212365. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Experimental models of skin inflammation.Clin Exp Allergy. 1999 Jul;29 Suppl 3:105-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.0290s3105.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999. PMID: 10444222 Review.
Cited by
-
Laser Doppler imager (LDI) scanner and intradermal injection for in vivo pharmacology in human skin microcirculation: responses to acetylcholine, endothelin-1 and their repeatability.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 May;59(5):511-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2004.02344.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15842548 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of topical sodium cromoglicate on itch and flare in human skin induced by intradermal histamine: a randomised double-blind vehicle controlled intra-subject design trial.BMC Res Notes. 2011 Mar 7;4:47. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-47. BMC Res Notes. 2011. PMID: 21385340 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Acupuncture in Itch: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Randomized Controlled Trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:208690. doi: 10.1155/2015/208690. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 26064156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling of histamine response measured by histamine iontophoresis laser Doppler.J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2016 Aug;43(4):385-93. doi: 10.1007/s10928-016-9478-9. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn. 2016. PMID: 27307292 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in treatment strategies for atopic dermatitis.Drugs. 2004;64(23):2639-66. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464230-00003. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15537368 Review.
References
-
- ARIYANAYAGAM M., BARLOW T.J.G., GRAHAM P., HALLSMITH S.P., HARRIS J.M. Topical sodium cromoglycate in the management of atopic eczema – a controlled trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 1985;112:343–348. - PubMed
-
- AUTY R.M. The clinical development of a new agent for the treatment of airway inflammation, nedocromil sodium (Tilade) Eur. J. Respir. Dis. 1986;69 Suppl 147:120–131. - PubMed
-
- CHUNG K.F. Effects of nedocromil sodium on airway neurogenic mechanisms. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1996;98:S112–S116. - PubMed
-
- CHURCH M.K., ELLATT S., OKAYAMA Y. Biological properties of human skin mast cells. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 1991;21 Suppl 3:1–9. - PubMed
-
- CLOUGH G.F., BENNETT A.R., CHURCH M.K. Effects of H-1 antagonists on the cutaneous vascular response to histamine and bradykinin: a study using scanning laser Doppler imaging. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998;138:806–814. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

