Neuropeptide Y changes the excitability of fine afferent units in the rat knee joint
- PMID: 11159723
- PMCID: PMC1572611
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0703871
Neuropeptide Y changes the excitability of fine afferent units in the rat knee joint
Abstract
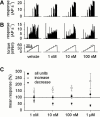
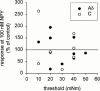
1. The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of the sympathetic co-transmitter Neuropeptide Y on primary afferent nerve fibres of the rat knee joint. The responses to passive joint rotations at defined torque were recorded from 41 slowly conducting afferent nerve fibres (0.9 - 18.8 m s(-1)) innervating the knee joint capsule. 2. About 70% of the joint afferents were significantly affected in their mechanosensitivity by topical application of Neuropeptide Y. Significant effects occurred at a concentration of 10 nM. 3. Decreased mechanosensitivity was observed in about 40% of nerve fibres, whereas 30% of the units increased the mechanosensitivity. In addition, in about 35% of the fibres resting activity was induced or increased. Neither the conduction velocity nor the mechanical threshold of the units correlated with the described effects of Neuropeptide Y. 4. NPY(13--36), a specific Y2-receptor agonist, only modulated the mechanosensitivity, with no effect on the resting activity. The effects on the mechanosensitivity were similar to Neuropeptide Y, i.e. increase and decrease of the response. 5. Studies with the Y1-agonist (Leu(31), Pro(34))-NPY showed that activation of the Y1-receptor predominantly resulted in an enhanced mechanosensitivity and an induction or increase of a resting activity. The opposite effect was observed by application of BIBP 3226 BS, a Y1-receptor antagonist. 6. In conclusion, these data indicate that Neuropeptide Y affects the excitability of sensory nerve fibre endings.
Figures
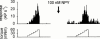


Similar articles
-
Frequency dependent changes in mechanosensitivity of rat knee joint afferents after antidromic saphenous nerve stimulation.Neuroscience. 2002;112(4):783-9. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00125-2. Neuroscience. 2002. PMID: 12088738
-
The neuropeptide Y (NPY) Y1 receptor antagonist BIBP 3226: equal effects on vascular responses to exogenous and endogenous NPY in the pig in vivo.Br J Pharmacol. 1997 Jun;121(3):595-603. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0701154. Br J Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9179405 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological characterization of the selective nonpeptide neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor antagonist BIBP 3226.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995 Oct;275(1):136-42. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995. PMID: 7562541
-
Neuropeptide Y Y1 receptor mechanisms in sympathetic vascular control.Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1997;636:1-55. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1997. PMID: 9179320 Review.
-
Peptidergic afferents: physiological aspects.Prog Brain Res. 1995;104:255-69. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61794-x. Prog Brain Res. 1995. PMID: 8552772 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Voltage-gated calcium channels may be involved in the regulation of the mechanosensitivity of slowly conducting knee joint afferents in rat.Exp Brain Res. 2003 Jun;150(3):379-84. doi: 10.1007/s00221-003-1465-x. Epub 2003 Apr 16. Exp Brain Res. 2003. PMID: 12698318
-
Sensory innervation of the dorsal longitudinal ligament and the meninges in the lumbar spine of the dog.Histochem Cell Biol. 2014 Oct;142(4):433-47. doi: 10.1007/s00418-014-1218-x. Epub 2014 Apr 20. Histochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24748503
-
Inhibitory effect of amiloride and gadolinium on fine afferent nerves in the rat knee: evidence of mechanogated ion channels in joints.Exp Brain Res. 2005 Nov;167(1):114-8. doi: 10.1007/s00221-005-0040-z. Epub 2005 Oct 29. Exp Brain Res. 2005. PMID: 16025293
References
-
- ABDULLA F., SMITH P. Nerve injury increases an excitatory action of neuropeptide Y and Y2-agonists on dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neuroscience. 1999a;89:43–60. - PubMed
-
- ABDULLA F., SMITH P. Neuropeptide Y actions and the distribution of Ca2+-dependent Cl- conductance in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J. Auto Nerv. Syst. 1999b;78:24–29. - PubMed
-
- AHMED M., SRINIVASAN G., THEODORSSON E., BJURHOLM A., KREICBERGS Extraction and quantitation of neuropeoptides in bone by radioimmunoassay. Regul. Pept. 1994;51:179–188. - PubMed
-
- BROQUA P., WETTSTEIN J., ROCHER M., GAUTHIER-MARTIN B., RIVIERE P., JUNIEN J., DAHL S. Antinociceptive effects of neuropeptide Y and related peptides in mice. Brain Research. 1996;724:25–32. - PubMed
-
- CALZA L., POZZA M., ZANNI M., MANZINI C., MANZINI E., HÖKFELT T. Peptide plasticity in primary sensory neurons and spinal cord during adjuvant-induced arthritis in the rat: an immunocytochemical and in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience. 1998;82:575–589. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

