Wnt signals from the neural tube block ectopic cardiogenesis
- PMID: 11159906
- PMCID: PMC312627
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.871501
Wnt signals from the neural tube block ectopic cardiogenesis
Abstract
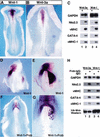
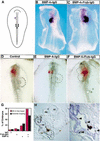
It has long been observed that repressive signals from the neural tube block cardiogenesis in vertebrates. Here we show that a signal from the neural tube that blocks cardiogenesis in the adjacent anterior paraxial mesoderm of stage 8-9 chick embryos can be mimicked by ectopic expression of either Wnt-3a or Wnt-1, both of which are expressed in the dorsal neural tube. Repression of cardiogenesis by the neural tube can be overcome by ectopic expression of a secreted Wnt antagonist. On the basis of both in vitro and in vivo results, we propose that Wnt signals from the neural tube normally act to block cardiogenesis in the adjacent anterior paraxial mesendoderm.
Figures

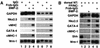

References
-
- Bhanot P, Brink M, Samos CH, Hsieh JC, Wang Y, Macke JP, Andrew D, Nathans J, Nusse R. A new member of the frizzled family from Drosophila functions as a Wingless receptor. Nature. 1996;382:225–230. - PubMed
-
- Christ B, Ordahl CP. Early stages of chick somite development. Anat Embryol. 1995;191:381–396. - PubMed
-
- Climent S, Sarasa M, Villar JM, Murillo-Ferrol NL. Neurogenic cells inhibit the differentiation of cardiogenic cells. Dev Biol. 1995;171:130–148. - PubMed
-
- Croissant JD, Carpenter S, Bader D. Identification and genomic cloning of CMHC1: A unique myosin heavy chain expressed exclusively in the developing chicken heart. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:1944–1951. - PubMed
-
- Frasch M. Induction of visceral and cardiac mesoderm by ectodermal Dpp in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1995;374:464–467. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
