Muscarinic regulation of dendritic and axonal outputs of rat thalamic interneurons: a new cellular mechanism for uncoupling distal dendrites
- PMID: 11160385
- PMCID: PMC6762242
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-04-01148.2001
Muscarinic regulation of dendritic and axonal outputs of rat thalamic interneurons: a new cellular mechanism for uncoupling distal dendrites
Abstract
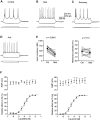
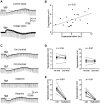
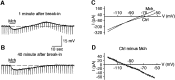
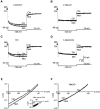
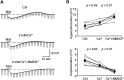
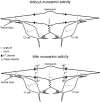
Inhibition is crucial for sharpening the sensory information relayed through the thalamus. To understand how the interneuron-mediated inhibition in the thalamus is regulated, we studied the muscarinic effects on interneurons in the lateral posterior nucleus and lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus. Here, we report that activation of muscarinic receptors switched the firing pattern in thalamic interneurons from bursting to tonic. Although neuromodulators switch the firing mode in several other types of neurons by altering their membrane potential, we found that activation of muscarinic subtype 2 receptors switched the fire mode in thalamic interneurons by selectively decreasing their input resistance. This is attributable to the muscarinic enhancement of a hyperpolarizing potassium conductance and two depolarizing cation conductances. The decrease in input resistance appeared to electrotonically uncouple the distal dendrites of thalamic interneurons, which effectively changed the inhibition pattern in thalamocortical cells. These results suggest a novel cellular mechanism for the cholinergic transformation of long-range, slow dendrite- and axon-originated inhibition into short-range, fast dendrite-originated inhibition in the thalamus observed in vivo. It is concluded that the electrotonic properties of the dendritic compartments of thalamic interneurons can be dynamically regulated by muscarinic activity.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Control of dendritic outputs of inhibitory interneurons in the lateral geniculate nucleus.Neuron. 2000 Sep;27(3):597-610. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)00069-6. Neuron. 2000. PMID: 11055441
-
Synaptic activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors regulates dendritic outputs of thalamic interneurons.Neuron. 2004 Feb 19;41(4):611-23. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(04)00013-3. Neuron. 2004. PMID: 14980209
-
Excitatory effects of thyrotropin-releasing hormone in the thalamus.J Neurosci. 2005 Feb 16;25(7):1664-73. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3198-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15716402 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate locally activates dendritic outputs of thalamic interneurons.Nature. 1998 Jul 30;394(6692):478-82. doi: 10.1038/28855. Nature. 1998. PMID: 9697770
-
Complex regulation of dendritic transmitter release from thalamic interneurons.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014 Dec;29:126-32. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2014.07.004. Epub 2014 Jul 23. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 25062503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Compartmentalized calcium dynamics in a C. elegans interneuron encode head movement.Nature. 2012 Jul 5;487(7405):99-103. doi: 10.1038/nature11081. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22722842 Free PMC article.
-
Postnatal development of GABAergic signalling in the rat lateral geniculate nucleus: presynaptic dendritic mechanisms.J Physiol. 2003 Jan 1;546(Pt 1):137-48. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.030643. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12509484 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct forms of cholinergic modulation in parallel thalamic sensory pathways.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Jan 6;101(1):320-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0304445101. Epub 2003 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 14691260 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of an Intrinsic Oscillation in Rat Geniculate Interneurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 8:2024.06.06.597830. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.06.597830. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38895250 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
The subcellular distribution of T-type Ca2+ channels in interneurons of the lateral geniculate nucleus.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 30;9(9):e107780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107780. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25268996 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahlsén G, Lindström S, Lo F-S. Interaction between inhibitory pathway to principal cells in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the cat. Exp Brain Res. 1985;58:134–143. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JS, Carandini M, Ferster D. Orientation tuning of input conductance, excitation, and inhibition in cat primary visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2000;84:909–926. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
