Antigenicity and immunogenicity of novel chimeric hepatitis B surface antigen particles with exposed hepatitis C virus epitopes
- PMID: 11160717
- PMCID: PMC114797
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.5.2130-2141.2001
Antigenicity and immunogenicity of novel chimeric hepatitis B surface antigen particles with exposed hepatitis C virus epitopes
Abstract
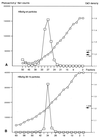
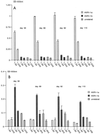
The small envelope protein of hepatitis B virus (HBsAg-S) can self-assemble into highly organized virus like particles (VLPs) and induce an effective immune response. In this study, a restriction enzyme site was engineered into the cDNA of HBsAg-S at a position corresponding to the exposed site within the hydrophilic a determinant region (amino acid [aa] 127-128) to create a novel HBsAg vaccine vector allowing surface orientation of the inserted sequence. We inserted sequences of various lengths from hypervariable region 1 (HVR1) of the hepatitis C virus (HCV) E2 protein containing immunodominant epitopes and demonstrated secretion of the recombinant HBsAg VLPs from transfected mammalian cells. A number of different recombinant proteins were synthesized, and HBsAg VLPs containing inserts up to 36 aa were secreted with an efficiency similar to that of wild-type HBsAg. The HVR1 region exposed on the particles retained an antigenic structure similar to that recognized immunologically during natural infection. VLPs containing epitopes from either HCV-1a or -1b strains were produced that induced strain-specific antibody responses in immunized mice. Injection of a combination of these VLPs induced antibodies against both HVR1 epitopes that resulted in higher titers than were achieved by vaccination with the individual VLPs, suggesting a synergistic effect. This may lead to the development of recombinant particles which are able to induce a broad anti-HCV immune response against the HCV quasispecies or other quasispecies-like infectious agents.
Figures



References
-
- Berger J, Hauber J, Hauber R, Geiger R, Cullen B R. Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eucaryotic cells. Gene. 1988;66:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Bruss V, Gerhardt E, Vieluf K, Wunderlich G. Functions of the large hepatitis B virus surface protein in viral particle morphogenesis. Intervirology. 1996;39:23–31. - PubMed
-
- Chengalvala M V, Bhat R A, Bhat B M, Vernon S K, Lubeck M D. Enhanced immunogenicity of hepatitis B surface antigen by insertion of a helper T cell epitope from tetanus toxoid. Vaccine. 1999;17:1035–1041. - PubMed
-
- Choo Q L, Kuo G, Ralston A, Weiner A, Chien D, Van Nest G, Han J, Berger K, Thudium K, Kuo C, Kansopon J, McFarland J, Tabrizi A, Ching K, Moss B, Cummins L B, Houghton M, Muchmore E. Vaccination of chimpanzees against infection by the hepatitis C virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994;91:1294–1298. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

