Mop3 is an essential component of the master circadian pacemaker in mammals
- PMID: 11163178
- PMCID: PMC3779439
- DOI: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)00205-1
Mop3 is an essential component of the master circadian pacemaker in mammals
Abstract
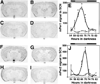
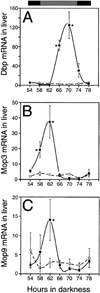
Circadian oscillations in mammalian physiology and behavior are regulated by an endogenous biological clock. Here we show that loss of the PAS protein MOP3 (also known as BMAL1) in mice results in immediate and complete loss of circadian rhythmicity in constant darkness. Additionally, locomotor activity in light-dark (LD) cycles is impaired and activity levels are reduced in Mop3-/- mice. Analysis of Period gene expression in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) indicates that these behavioral phenotypes arise from loss of circadian function at the molecular level. These results provide genetic evidence that MOP3 is the bona fide heterodimeric partner of mCLOCK. Furthermore, these data demonstrate that MOP3 is a nonredundant and essential component of the circadian pacemaker in mammals.
Figures


References
-
- Allada R, White NE, So WV, Hall JC, Rosbash M. A mutant Drosophila homolog of mammalian Clock disrupts circadian rhythms and transcription of period and timeless. Cell. 1998;93:791–804. - PubMed
-
- Ceriani MF, Darlington TK, Staknis D, Mas P, Petti AA, Weitz CJ, Kay SA. Light-dependent sequestration of TIMELESS by CRYPTOCHROME. Science. 1999;285:553–556. - PubMed
-
- Darlington TK, Wager-Smith K, Ceriani MF, Staknis D, Gekakis N, Steeves TDL, Weitz CJ, Takahashi JS, Kay SA. Closing the circadian loop: CLOCK-induced transcription of its own inhibitors per and tim. Science. 1998;280:1599–1603. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

