Population modelling of the effect of inogatran, at thrombin inhibitor, on ex vivo coagulation time (APTT) in healthy subjects and patients with coronary artery disease
- PMID: 11167667
- PMCID: PMC2014429
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.01326.x
Population modelling of the effect of inogatran, at thrombin inhibitor, on ex vivo coagulation time (APTT) in healthy subjects and patients with coronary artery disease
Abstract
Aims: The purpose of this study was to characterize the relationship between the degree of anticoagulation, assessed by APTT, and the plasma concentration of inogatran in healthy subjects and in patients with coronary artery disease.
Methods: Data from five phase I studies in 78 healthy males and two phase II multicentre studies in 948 patients of both sexes with unstable angina pectoris or non-Q-wave myocardial infarction were evaluated. A total of 3296 pairs of concentration-APTT samples were obtained before, during, and after intravenous infusions of inogatran. Mixed effects modelling was used for population pharmacodynamic analysis of the drug effect and for describing the variability in baseline APTT.
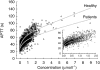
Results: The population mean baseline APTT was 29 s, but large variations between individuals (s.d. 3.6 s) were observed. The variability between studies (1.3 s) and centres (1.8 s) were of less importance, though statistically significant. APTT increased in a nonlinear manner with increasing inogatran concentration and the relationship was well described by a combined linear and Emax model. A significant part of the overall variability could be ascribed to the APTT reagent and equipment used at the different study centres. These method-dependent differences were compensated for by including the lower limit of the normal reference range as a covariate, affecting both baseline and Emax, in the model. For the typical healthy subject and patient, the method-corrected population mean parameters were: APTTbaseline 35 and 31 s, slope 8.0 and 5.8 s x l x micromol(-1), Emax 36 and 34 s, and EC50 0.54 and 0.72 micromol x l(-1), respectively. The model predicted plasma concentration needed to double the APTT from the baseline value was 1.25 and 1.45 micromol x l(-1) in the healthy volunteer and patient, respectively.
Conclusions: The nonlinear relationship between APTT and inogatran concentration in plasma was well described by a combined linear and Emax model. Pooling of data was made possible by incorporating a centre-specific characteristic of the assay method in the model. Patients had lower baseline APTT and appeared to have less pronounced effect of inogatran than young healthy subjects.
Figures
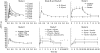
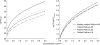
Similar articles
-
Dose-effect relationship for several coagulation markers during administration of the direct thrombin inhibitor S 18326 in healthy subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Feb;53(2):147-54. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01534.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11851638 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Activated partial thromboplastin time and clinical outcome after thrombin inhibition in unstable coronary artery disease.Eur Heart J. 1999 Nov;20(22):1657-66. doi: 10.1053/euhj.1999.1750. Eur Heart J. 1999. PMID: 10543929 Clinical Trial.
-
A low molecular weight, selective thrombin inhibitor, inogatran, vs heparin, in unstable coronary artery disease in 1209 patients. A double-blind, randomized, dose-finding study. Thrombin inhibition in Myocardial Ischaemia (TRIM) study group.Eur Heart J. 1997 Sep;18(9):1416-25. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.eurheartj.a015467. Eur Heart J. 1997. PMID: 9458447 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of a low molecular mass thrombin inhibitor, inogatran, and heparin on thrombin generation and fibrin turnover in patients with unstable coronary artery disease.Eur Heart J. 1999 Apr;20(7):506-18. doi: 10.1053/euhj.1998.1336. Eur Heart J. 1999. PMID: 10365287 Clinical Trial.
-
Thrombin inhibition with inogatran for unstable angina pectoris: evidence for reactivated ischaemia after cessation of short-term treatment.Coron Artery Dis. 1996 Sep;7(9):673-81. doi: 10.1097/00019501-199609000-00009. Coron Artery Dis. 1996. PMID: 8950498 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Population pharmacokinetics of metformin in healthy subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: simulation of doses according to renal function.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013 May;52(5):373-84. doi: 10.1007/s40262-013-0046-9. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2013. PMID: 23475568 Clinical Trial.
-
Dose-effect relationship for several coagulation markers during administration of the direct thrombin inhibitor S 18326 in healthy subjects.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002 Feb;53(2):147-54. doi: 10.1046/j.0306-5251.2001.01534.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11851638 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Delayed concentration effect models for dabigatran anticoagulation.Paediatr Anaesth. 2022 Oct;32(10):1113-1120. doi: 10.1111/pan.14511. Epub 2022 Jul 2. Paediatr Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 35735989 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the direct oral thrombin inhibitor dabigatran in healthy elderly subjects.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47(1):47-59. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200847010-00005. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008. PMID: 18076218 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran on ex vivo coagulation time in orthopaedic surgery patients: a population model analysis.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006 Nov;62(5):527-37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2006.02667.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 17061960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mann KG. Prothrombin and thrombin. In: Colman RW, Hirsh J, Marder VJ, Salzman EW, editors. Hemostasis and Thrombosis: Basic Principles and Clinical Practice. 3. Philadelphia: JB Lippincott; 1994. pp. 71–79.
-
- Teger-Nilsson A-C, Bylund R, Gustafsson D, Gyzander E, Eriksson U. In vitro effects of inogatran, a selective low molecular weight thrombin inhibitor. Thromb Res. 1997;85:133–145. 10.1016/s0049-3848(96)00230-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kher A, Dieri RA, Hemker HC, Béguin S. Laboratory assessment of antithrombotic therapy: What tests and if so why? Haemostasis. 1997;27:211–218. - PubMed
-
- Antman EM for the TIMI; A Investigators. Hirudin in acute myocardial infarction. Safety report from the thrombolysis and thrombin inhibition in myocardial infarction (TIMI) 9A trial. Circulation. 1994;90:1624–1630. - PubMed
-
- Clarke RJ, Mayo RN, Fitzgerald GA, Fitzgerald DJ. Combined administration of aspirin and a specific thrombin inhibitor in man. Circulation. 1991;83:1510–1518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

