Adrenalectomy enhances response of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) to haemorrhage in the conscious rat
- PMID: 11167993
- PMCID: PMC1905961
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01444.x
Adrenalectomy enhances response of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) to haemorrhage in the conscious rat
Abstract
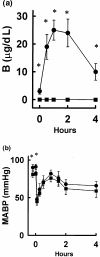
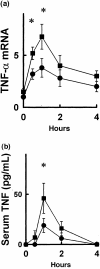
Several factors have been implicated in TNF-alpha induction after haemorrhage, but the precise mechanism is unknown. To assess a possible role of adrenal glands on TNF-alpha induction after haemorrhage, adrenalectomized (ADX) and sham-adrenalectomized (Sham) rats were subjected to 20 ml/kg haemorrhage (approximately 30% of the total blood volume) over 5 min in the conscious state, and changes in serum TNF and hepatic TNF-alpha mRNA were analysed by cytotoxicity against L929 cells and by semiquantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, respectively. Changes in plasma corticosterone (CS) and mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) were also detected. Plasma CS levels showed a rapid increase after haemorrhage in Sham rats, whereas there was no response in ADX rats. Responses of MABP were comparable in the two groups. Both serum TNF and hepatic TNF-alpha mRNA showed rapid increases after haemorrhage in the Sham group, and these increases were significantly augmented in the ADX group. Pretreatment with CS (100 microg/h) negated these augmentations in ADX rats. These results show that adrenalectomy enhances the response of TNF-alpha to 20 ml/kg haemorrhage in the conscious rat, and suggest that endogenous glucocorticoids may play an inhibitory role in the induction of TNF-alpha after haemorrhage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Responses of hepatic TNF-alpha mRNA to repeated hemorrhage in the conscious rat.Am J Physiol. 1998 Jul;275(1):E27-31. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1998.275.1.E27. Am J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9688870
-
The role of tumour necrosis factor-alpha in renal dysfunction following mild haemorrhage in rats.Int J Exp Pathol. 2004 Dec;85(6):345-53. doi: 10.1111/j.0959-9673.2004.00403.x. Int J Exp Pathol. 2004. PMID: 15566431 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxyurea induces the gene expression and synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines in vivo.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997 Jan;280(1):477-82. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1997. PMID: 8996231
-
Corticotrope response to removal of releasing factors and corticosteroids in vivo.Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2190-7. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2190. Endocrinology. 1985. PMID: 2995008
-
Role of glucocorticoids in the response of the hypothalamo-corticotrope, immune and adipose systems to repeated endotoxin administration.Neuroendocrinology. 1999 May;69(5):360-9. doi: 10.1159/000054438. Neuroendocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10343177
References
-
- Aggarwal BB, Puri RK. Common and uncommon features of cytokines and cytokine receptors: an overview. In: Aggarwal BB, Puri RK, editors. Human cytokines. Cambridge: Blackwell Science; 1995. pp. 3–24.
-
- Barahmi S, Yao YM, Leichtfried G, Redl H, Marzi I, Schlag G. Significance of TNF in hemorrhage-related hemodynamic alterations, organ injury, and mortality in rats. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:H2219–26. - PubMed
-
- Chaudry IH, Ayala A, Ertel W, Stephan RN. Hemorrhage and resuscitation: immunological aspects. Am J Physiol. 1990;259:R663–78. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita M, Yamashita M. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment attenuates cytokine induction after massive hemorrhage. Am J Physiol. 2000;278:E811–6. - PubMed
-
- Yamashita M. Bactericidal/permeability-increasing protein ameliorates hypercoagulability after hemorrhagic shock. Thromb Res. 1997;87:323–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

