Dual modulation of cell survival and cell death by beta(2)-adrenergic signaling in adult mouse cardiac myocytes
- PMID: 11171998
- PMCID: PMC29304
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.1607
Dual modulation of cell survival and cell death by beta(2)-adrenergic signaling in adult mouse cardiac myocytes
Abstract
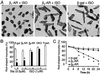
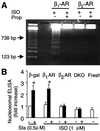
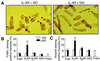
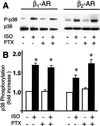
The goal of this study was to determine whether beta(1)-adrenergic receptor (AR) and beta(2)-AR differ in regulating cardiomyocyte survival and apoptosis and, if so, to explore underlying mechanisms. One potential mechanism is that cardiac beta(2)-AR can activate both G(s) and G(i) proteins, whereas cardiac beta(1)-AR couples only to G(s). To avoid complicated crosstalk between beta-AR subtypes, we expressed beta(1)-AR or beta(2)-AR individually in adult beta(1)/beta(2)-AR double knockout mouse cardiac myocytes by using adenoviral gene transfer. Stimulation of beta(1)-AR, but not beta(2)-AR, markedly induced myocyte apoptosis, as indicated by increased terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase-mediated UTP end labeling or Hoechst staining positive cells and DNA fragmentation. In contrast, beta(2)-AR (but not beta(1)-AR) stimulation elevated the activity of Akt, a powerful survival signal; this effect was fully abolished by inhibiting G(i), G(beta gamma), or phosphoinositide 3 kinase (PI3K) with pertussis toxin, beta ARK-ct (a peptide inhibitor of G(beta gamma)), or LY294002, respectively. This indicates that beta(2)-AR activates Akt via a G(i)-G(beta gamma)-PI3K pathway. More importantly, inhibition of the G(i)-G(beta gamma)-PI3K-Akt pathway converts beta(2)-AR signaling from survival to apoptotic. Thus, stimulation of a single class of receptors, beta(2)-ARs, elicits concurrent apoptotic and survival signals in cardiac myocytes. The survival effect appears to predominate and is mediated by the G(i)-G(beta gamma)-PI3K-Akt signaling pathway.
Figures


References
-
- Narula J, Haider N, Virmani R, DiSalvo T G, Kolodgie F D, Hajjar R J, Schmidt U, Semigran M J, Dec G W, Khaw B A. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1182–1189. - PubMed
-
- Olivetti G, Abbi R, Quaini F, Kajstura J, Cheng W, Nitahara J A, Quaini E, Di Loreto C, Beltrami C A, Kratjewski S, et al. N Engl J Med. 1997;336:1131–1141. - PubMed
-
- Olivetti G, Quaini F, Sala R, Lagrasta C, Corradi D, Bonacina E, Gambert S R, Cigola E, Anversa P. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1996;28:2005–2016. - PubMed
-
- Li Z, Bing O H, Long X, Robinson K G, Lakatta E G. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:H2313–H2319. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

