Eight novel families of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae
- PMID: 11172014
- PMCID: PMC29320
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.98.4.1699
Eight novel families of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae
Abstract
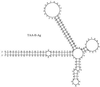
Eight novel families of miniature inverted repeat transposable elements (MITEs) were discovered in the African malaria mosquito, Anopheles gambiae, by using new software designed to rapidly identify MITE-like sequences based on their structural characteristics. Divergent subfamilies have been found in two families. Past mobility was demonstrated by evidence of MITE insertions that resulted in the duplication of specific TA, TAA, or 8-bp targets. Some of these MITEs share the same target duplications and similar terminal sequences with MITEs and other DNA transposons in human and other organisms. MITEs in A. gambiae range from 40 to 1340 copies per genome, much less abundant than MITEs in the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Statistical analyses suggest that most A. gambiae MITEs are in highly AT-rich regions, many of which are closely associated with each other. The analyses of these novel MITEs underscored interesting questions regarding their diversity, origin, evolution, and relationships to the host genomes. The discovery of diverse families of MITEs in A. gambiae has important practical implications in light of current efforts to control malaria by replacing vector mosquitoes with genetically modified refractory mosquitoes. Finally, the systematic approach to rapidly identify novel MITEs should have broad applications for the analysis of the ever-growing sequence databases of a wide range of organisms.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

