Isolation and characterization of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from primary culture--primary culture cells markedly differ from fourth-passage cells
- PMID: 11178129
- PMCID: PMC17827
- DOI: 10.1186/ar142
Isolation and characterization of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from primary culture--primary culture cells markedly differ from fourth-passage cells
Abstract
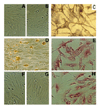
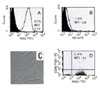
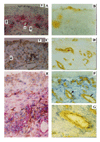
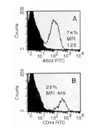
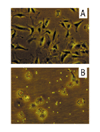
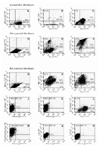
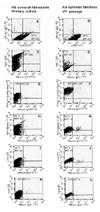
To reduce culture artifacts by conventional repeated passaging and long-term culture in vitro, the isolation of synovial fibroblasts (SFB) was attempted from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial membranes by trypsin/collagenase digest, short-term in vitro adherence (7 days), and negative isolation using magnetobead-coupled anti-CD14 monoclonal antibodies. This method yielded highly enriched SFB (85% prolyl-4-hydroxylase+/74% Thy-1/CD90+ cells; <2% contaminating macrophages; <1% leukocytes/endothelial cells) that, in comparison with conventional fourth-passage RA-SFB, showed a markedly different phenotype and significantly lower proliferation rates upon stimulation with platelet-derived growth factor and IL-1beta. This isolation method is simple and reliable, and may yield cells with features closer to the in vivo configuration of RA-SFB by avoiding extended in vitro culture.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cytokine mRNA and protein expression in primary-culture and repeated-passage synovial fibroblasts from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res. 2002;4(2):117-25. doi: 10.1186/ar391. Epub 2001 Nov 8. Arthritis Res. 2002. PMID: 11879547 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition, culture, and phenotyping of synovial fibroblasts.Methods Mol Med. 2007;135:365-75. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-401-8_24. Methods Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17951672
-
Amplification of the synovial inflammatory response through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor kappaB using ligation of CD40 on CD14+ synovial cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2004 Jul;50(7):2167-77. doi: 10.1002/art.20340. Arthritis Rheum. 2004. PMID: 15248214
-
Origins of fibroblasts in rheumatoid synovial tissues: Implications from organ fibrotic models.Mod Rheumatol. 2018 Jul;28(4):579-582. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2017.1386837. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Mod Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29067846 Review.
-
A question of transformation: the synovial fibroblast in rheumatoid arthritis.Am J Pathol. 2003 May;162(5):1399-402. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64272-1. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12707022 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Cytokine mRNA and protein expression in primary-culture and repeated-passage synovial fibroblasts from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res. 2002;4(2):117-25. doi: 10.1186/ar391. Epub 2001 Nov 8. Arthritis Res. 2002. PMID: 11879547 Free PMC article.
-
Adapted Boolean network models for extracellular matrix formation.BMC Syst Biol. 2009 Jul 21;3:77. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-3-77. BMC Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19622164 Free PMC article.
-
Thy1 (CD90) Expression Is Elevated in Radiation-Induced Periprosthetic Capsular Contracture: Implication for Novel Therapeutics.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Aug;140(2):316-326. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000003542. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017. PMID: 28746279 Free PMC article.
-
Batch correction of microarray data substantially improves the identification of genes differentially expressed in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.BMC Med Genomics. 2012 Jun 8;5:23. doi: 10.1186/1755-8794-5-23. BMC Med Genomics. 2012. PMID: 22682473 Free PMC article.
-
The production of CXCR3-agonistic chemokines by synovial fibroblasts from patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2005 Jun;25(5):361-7. doi: 10.1007/s00296-004-0449-x. Epub 2004 Mar 5. Rheumatol Int. 2005. PMID: 15004722
References
-
- Firestein GS. Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:1781–1790. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS, Alvaro-Gracia JM, Maki R. Quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1990;144:3347–3353. - PubMed
-
- Faßbender HG. Histomorphological basis of articular cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Coll Relat Res. 1983;3:141–155. - PubMed
-
- Lafyatis R, Remmers EF, Roberts AB, Yocum DE, Sporn MB, Wilder RL. Anchorage-independent growth of synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints. Stimulation by exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids. J Clin Invest. 1989;83:1267–1276. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

