Isolation and characterization of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from primary culture--primary culture cells markedly differ from fourth-passage cells
- PMID: 11178129
- PMCID: PMC17827
- DOI: 10.1186/ar142
Isolation and characterization of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts from primary culture--primary culture cells markedly differ from fourth-passage cells
Abstract
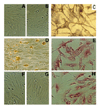
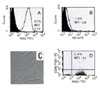
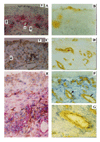
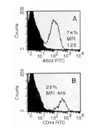
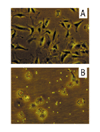
To reduce culture artifacts by conventional repeated passaging and long-term culture in vitro, the isolation of synovial fibroblasts (SFB) was attempted from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial membranes by trypsin/collagenase digest, short-term in vitro adherence (7 days), and negative isolation using magnetobead-coupled anti-CD14 monoclonal antibodies. This method yielded highly enriched SFB (85% prolyl-4-hydroxylase+/74% Thy-1/CD90+ cells; <2% contaminating macrophages; <1% leukocytes/endothelial cells) that, in comparison with conventional fourth-passage RA-SFB, showed a markedly different phenotype and significantly lower proliferation rates upon stimulation with platelet-derived growth factor and IL-1beta. This isolation method is simple and reliable, and may yield cells with features closer to the in vivo configuration of RA-SFB by avoiding extended in vitro culture.
Figures

References
-
- Firestein GS. Invasive fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Passive responders or transformed aggressors? Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39:1781–1790. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS, Alvaro-Gracia JM, Maki R. Quantitative analysis of cytokine gene expression in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1990;144:3347–3353. - PubMed
-
- Faßbender HG. Histomorphological basis of articular cartilage destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Coll Relat Res. 1983;3:141–155. - PubMed
-
- Lafyatis R, Remmers EF, Roberts AB, Yocum DE, Sporn MB, Wilder RL. Anchorage-independent growth of synoviocytes from arthritic and normal joints. Stimulation by exogenous platelet-derived growth factor and inhibition by transforming growth factor-beta and retinoids. J Clin Invest. 1989;83:1267–1276. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

