Higher plant cellulose synthases
- PMID: 11178255
- PMCID: PMC138876
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2000-1-4-reviews3001
Higher plant cellulose synthases
Abstract
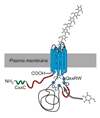
Cellulose, an aggregate of unbranched polymers of beta-1,4-linked glucose residues, is the major component of wood and thus paper, and is synthesized by plants, most algae, some bacteria and fungi, and even some animals. The genes that synthesize cellulose in higher plants differ greatly from the well-characterized genes found in Acetobacter and Agrobacterium sp. More correctly designated as 'cellulose synthase catalytic subunits', plant cellulose synthase (CesA) proteins are integral membrane proteins, approximately 1,000 amino acids in length. The sequences for more than 20 full-length CesA genes are available, and they show high similarity to one another across the entire length of the encoded protein, except for two small regions of variability. There are a number of highly conserved residues, including several motifs shown to be necessary for processive glycosyltransferase activity. No crystal structure is known for cellulose synthase proteins, and the exact enzymatic mechanism is unknown. There are a number of mutations in cellulose synthase genes in the model organism Arabidopsis thaliana. Some of these mutants show altered morphology due to the lack of a properly developed primary or secondary cell wall. Others show resistance to well-characterized cellulose biosynthesis inhibitors.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Beta-D-glycan synthases and the CesA gene family: lessons to be learned from the mixed-linkage (1-->3),(1-->4)beta-D-glucan synthase.Plant Mol Biol. 2001 Sep;47(1-2):145-60. Plant Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11554469
-
Endosidin20 Targets the Cellulose Synthase Catalytic Domain to Inhibit Cellulose Biosynthesis.Plant Cell. 2020 Jul;32(7):2141-2157. doi: 10.1105/tpc.20.00202. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Plant Cell. 2020. PMID: 32327535 Free PMC article.
-
The valine and lysine residues in the conserved FxVTxK motif are important for the function of phylogenetically distant plant cellulose synthases.Glycobiology. 2016 May;26(5):509-19. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwv118. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Glycobiology. 2016. PMID: 26646446
-
Updating Insights into the Catalytic Domain Properties of Plant Cellulose synthase (CesA) and Cellulose synthase-like (Csl) Proteins.Molecules. 2021 Jul 17;26(14):4335. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144335. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299608 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plant cellulose synthesis: CESA proteins crossing kingdoms.Phytochemistry. 2015 Apr;112:91-9. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2014.07.009. Epub 2014 Aug 4. Phytochemistry. 2015. PMID: 25104231 Review.
Cited by
-
The cellulose synthase (CESA) gene superfamily of the moss Physcomitrella patens.Plant Mol Biol. 2007 Jan;63(2):207-19. doi: 10.1007/s11103-006-9083-1. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Plant Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17006591
-
The papain-like cysteine protease CEP1 is involved in programmed cell death and secondary wall thickening during xylem development in Arabidopsis.J Exp Bot. 2019 Jan 1;70(1):205-215. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ery356. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30376110 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the molecular mechanism underlying the intimate relationship between cellulose microfibrils and cortical microtubules.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Mar 13;5:90. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00090. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24659994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KOBITO1 encodes a novel plasma membrane protein necessary for normal synthesis of cellulose during cell expansion in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2002 Sep;14(9):2001-13. doi: 10.1105/tpc.002873. Plant Cell. 2002. PMID: 12215501 Free PMC article.
-
PhCESA3 silencing inhibits elongation and stimulates radial expansion in petunia.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 2;7:41471. doi: 10.1038/srep41471. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28150693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pear JR, Kawagoe Y, Schreckengost WE, Delmer DP, Stalker DM. Higher plants contain homologs of the bacterial celA genes encoding the catalytic subunit of cellulose synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA . 1996;93:12637–12642. This paper describes the cloning of the first plant cellulose synthase gene. Although this paper shows a great deal of experimental evidence that these genes are the cellulose synthase catalytic subunits, the genetic proof was presented by Arioli et al. [7]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campbell JA, Davies GJ, Bulone V, Henrissat B. A classification of nucleotide-diphospho-sugar glycosyltransferases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem J. 1997;326:929–939. A descriptive paper demonstrating the classification of glycosyltransferases into families based on amino acid sequence. The cellulose synthases belong to family 2, a family containing proteins from many different species of plants, animals, bacteria and fungi (see [3]). The tables from this paper are continually updated (see [12]). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Glycosyltransferase 2 family http://afmb.cnrs-mrs.fr/~pedro/CAZY/gtf_2.html
-
- Cellwall.stanford.edu http://cellwall.stanford.edu. A sequence resource for plant cell wall biologists interested in polysaccharide biosynthesis. This site collects, organizes and summarizes sequence information for all cellulose synthase and cellulose synthase-like genes in higher plants.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

