Can sequence determine function?
- PMID: 11178260
- PMCID: PMC138884
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2000-1-5-reviews0005
Can sequence determine function?
Abstract
The functional annotation of proteins identified in genome sequencing projects is based on similarities to homologs in the databases. As a result of the possible strategies for divergent evolution, homologous enzymes frequently do not catalyze the same reaction, and we conclude that assignment of function from sequence information alone should be viewed with some skepticism.
Figures

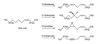

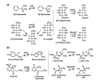
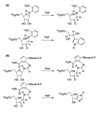
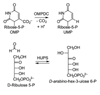
References
-
- Blattner FR, Plunkett G, 3rd, Bloch CA, Perna NT, Burland V, Riley M, Collado-Vides J, Glasner JD, Rode CK, Mayhew GF, et al. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–1474. - PubMed
-
- Kunst F, Ogasawara N, Moszer I, Albertini AM, Alloni G, Azevedo V, Bertero MG, Bessieres P, Bolotin A, Borchert S, et al. The complete genome sequence of the gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1997;390:249–256. - PubMed
-
- Eisen JA. Phylogenomics: improving functional predictions for uncharacterized genes by evolutionary analysis. Genome Res. 1998;8:163–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

