A search for reverse transcriptase-coding sequences reveals new non-LTR retrotransposons in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 11178266
- PMCID: PMC16141
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2000-1-6-research0012
A search for reverse transcriptase-coding sequences reveals new non-LTR retrotransposons in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
Background: Non-long terminal repeat (non-LTR) retrotransposons are eukaryotic mobile genetic elements that transpose by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. We have performed a systematic search for sequences matching the characteristic reverse transcriptase domain of non-LTR retrotransposons in the sequenced regions of the Drosophila melanogaster genome.
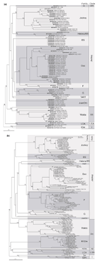
Results: In addition to previously characterized BS, Doc, F, G, I and Jockey elements, we have identified new non-LTR retrotransposons: Waldo, You and JuanDm. Waldo elements are related to mosquito RTI elements. You to the Drosophila I factor, and JuanDm to mosquito Juan-A and Juan-C. Interestingly, all JuanDm elements are highly homogeneous in sequence, suggesting that they are recent components of the Drosophila genome.
Conclusions: The genome of D. melanogaster contains at least ten families of non-site-specific non-LTR retrotransposons representing three distinct clades. Many of these families contain potentially active members. Fine evolutionary analyses must await the more accurate sequences that are expected in the next future.
Figures





References
-
- Eickbush TH. Transposing without ends: the non-LTR retrotransposable elements. New Biol. 1992;4:430–440. - PubMed
-
- Malik HS, Burke WD, Eickbush TH. The age and evolution of non-LTR retrotransposable elements. Mol Biol Evol. 1999;16:793–805. - PubMed
-
- Jakubczak JL, Xiong Y, Eickbush TH. Type I (R1) and type II (R2) ribosomal DNA insertions of Drosophila melanogaster are retrotransposable elements closely related to those of Bombyx mori. J Mol Biol. 1990;212:37–52. - PubMed
-
- Xiong YE, Eickbush TH. Functional expression of a sequence-specific endonuclease encoded by the retrotransposon R2Bm. Cell. 1988;55:235–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

