Analyses of the effects that disease-causing missense mutations have on the structure and function of the winged-helix protein FOXC1
- PMID: 11179011
- PMCID: PMC1274476
- DOI: 10.1086/318792
Analyses of the effects that disease-causing missense mutations have on the structure and function of the winged-helix protein FOXC1
Abstract
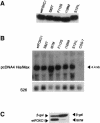
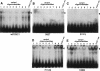
Five missense mutations of the winged-helix FOXC1 transcription factor, found in patients with Axenfeld-Rieger (AR) malformations, were investigated for their effects on FOXC1 structure and function. Molecular modeling of the FOXC1 forkhead domain predicted that the missense mutations did not alter FOXC1 structure. Biochemical analyses indicated that, whereas all mutant proteins correctly localize to the cell nucleus, the I87M mutation reduced FOXC1-protein levels. DNA-binding experiments revealed that, although the S82T and S131L mutations decreased DNA binding, the F112S and I126M mutations did not. However, the F112S and I126M mutations decrease the transactivation ability of FOXC1. All the FOXC1 mutations had the net effect of reducing FOXC1 transactivation ability. These results indicate that the FOXC1 forkhead domain contains separable DNA-binding and transactivation functions. In addition, these findings demonstrate that reduced stability, DNA binding, or transactivation, all causing a decrease in the ability of FOXC1 to transactivate genes, can underlie AR malformations.
Figures





References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) Databases, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Database/index.html (for human FOXC1 [AF048693], mouse Foxc1 [NM008592], human FOXC2 [Y08223], human FOXD1 [U13222], human FOXE1 [U89995], human FOXF1 [U13219], human FOXF2 [U13220], human HFH1 [AF153341], human FOXH1 [AF076292], mouse Foxh2 [AF110506], and rat Genesis/Foxd3 [NM012183])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for FOXC1 [MIM 601090], PITX2 [MIM 601542], Oct1 [MIM 602607], and FOXC2 [MIM 602402])
References
-
- Alward WL, Semina EV, Kalenak JW, Heon E, Sheth BP, Stone EM, Murray JC (1998) Autosomal dominant iris hypoplasia is caused by a mutation in the Rieger syndrome (RIEG/PITX2) gene. Am J Ophthalmol 125:98–100 - PubMed
-
- Becker R, Chambers J, Wilks A (1988) The new S language—a programming environment for data analysis and graphics. Wadsworth, Pacific Grove, CA
-
- Bryant SH, Lawrence CE (1993) An empirical energy function for threading protein sequence through the folding motif. Proteins 16:92–112 - PubMed
-
- Fetrow J, Bryant SH (1993) New programs for protein tertiary structure prediction. Biotechnology 11:479–484 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

