Familial dysautonomia is caused by mutations of the IKAP gene
- PMID: 11179021
- PMCID: PMC1274486
- DOI: 10.1086/318808
Familial dysautonomia is caused by mutations of the IKAP gene
Abstract
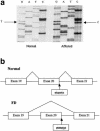
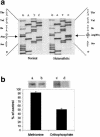
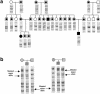
The defective gene DYS, which is responsible for familial dysautonomia (FD) and has been mapped to a 0.5-cM region on chromosome 9q31, has eluded identification. We identified and characterized the RNAs encoded by this region of chromosome 9 in cell lines derived from individuals homozygous for the major FD haplotype, and we observed that the RNA encoding the IkappaB kinase complex-associated protein (IKAP) lacks exon 20 and, as a result of a frameshift, encodes a truncated protein. Sequence analysis reveals a T-->C transition in the donor splice site of intron 20. In individuals bearing a minor FD haplotype, a missense mutation in exon 19 disrupts a consensus serine/threonine kinase phosphorylation site. This mutation results in defective phosphorylation of IKAP. These mutations were observed to be present in a random sample of Ashkenazi Jewish individuals, at approximately the predicted carrier frequency of FD. These findings demonstrate that mutations in the gene encoding IKAP are responsible for FD.
Figures

References
Electronic-Database Information
-
- Genbank, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank/ (for IKAP cDNA [accession number NM_003640])
-
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM), http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Omim/ (for hereditary sensory neuropathy type III [MIM 223900])
References
-
- Axelrod FB (1996) Familial dysautonomia. In: Robertson D, Low PA, Polinsky RJ (eds) Primer on the autonomic nervous system. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 242–249
-
- Axelrod FB, Nachtigal R, Dancis J (1974) Familial dysautonomia: diagnosis, pathogenesis and management. Adv Pediatr 21:75–96 - PubMed
-
- Blumenfeld A, Slaugenhaupt SA, Liebert CB, Temper V, Maayan C, Gill S, Lucente DE, Idelson M, MacCormack K, Monahan MA, Mull J, Leyne M, Mendillo M, Schiripo T, Mishori E, Breakefield X, Axelrod FB, Gusella JF (1999) Precise genetic mapping and haplotype analysis of the familial dysautonomia gene on human chromosome 9q31. Am J Hum Genet 64:1110–1118 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breakefield XO, Ozelius L, Bothwell MA, Chao MV, Axelrod F, Kramer PL, Kidd KK, et al (1986) DNA polymorphisms for the nerve growth factor receptor gene exclude its role in familial dysautonomia. Mol Biol Med 3:483–94 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

