Rab-interacting lysosomal protein (RILP): the Rab7 effector required for transport to lysosomes
- PMID: 11179213
- PMCID: PMC145419
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.4.683
Rab-interacting lysosomal protein (RILP): the Rab7 effector required for transport to lysosomes
Abstract
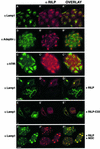
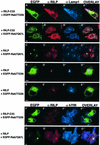
Rab7 is a small GTPase that controls transport to endocytic degradative compartments. Here we report the identification of a novel 45 kDa protein that specifically binds Rab7GTP at its C-terminus. This protein contains a domain comprising two coiled-coil regions typical of myosin-like proteins and is found mainly in the cytosol. We named it RILP (Rab-interacting lysosomal protein) since it can be recruited efficiently on late endosomal and lysosomal membranes by Rab7GTP. RILP-C33 (a truncated form of the protein lacking the N-terminal half) strongly inhibits epidermal growth factor and low-density lipoprotein degradation, and causes dispersion of lysosomes similarly to Rab7 dominant-negative mutants. More importantly, expression of RILP reverses/prevents the effects of Rab7 dominant-negative mutants. All these data are consistent with a model in which RILP represents a downstream effector for Rab7 and both proteins act together in the regulation of late endocytic traffic.
Figures





References
-
- Bartel P.L., Chien,C.-T., Sternglanz,R. and Fields,S. (1993) Using the two-hybrid system to detect protein–protein interactions. In Hartley,D.A. (ed.), Cellular Interaction in Development: A Practical Approach. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, pp. 153–179.
-
- Bretscher A. (1999) Regulation of cortical structure by the ezrin–radixin–moesin protein family. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 11, 109–116. - PubMed
-
- Brown M.S. and Goldstein,J.L. (1975) Regulation of the activity of the low density lipoprotein receptor in human fibroblasts. Cell, 6, 307–316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

