Use of a whole genome approach to identify vaccine molecules affording protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection
- PMID: 11179332
- PMCID: PMC98061
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.69.3.1593-1598.2001
Use of a whole genome approach to identify vaccine molecules affording protection against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection
Abstract
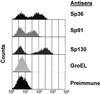
Microbial targets for protective humoral immunity are typically surface-localized proteins and contain common sequence motifs related to their secretion or surface binding. Exploiting the whole genome sequence of the human bacterial pathogen Streptococcus pneumoniae, we identified 130 open reading frames encoding proteins with secretion motifs or similarity to predicted virulence factors. Mice were immunized with 108 of these proteins, and 6 conferred protection against disseminated S. pneumoniae infection. Flow cytometry confirmed the surface localization of several of these targets. Each of the six protective antigens showed broad strain distribution and immunogenicity during human infection. Our results validate the use of a genomic approach for the identification of novel microbial targets that elicit a protective immune response. These new antigens may play a role in the development of improved vaccines against S. pneumoniae.
Figures

References
-
- Austrian R. The pneumococcus at the millennium: not down, not out. J Infect Dis. 1999;179(Suppl. 2):S338–S441. - PubMed
-
- Baltz R H, Norris F H, Matsushima P, DeHoff B S, Rockey P, Porter G, Burgett S, Peery R, Hoskins J, Braverman L, Jenkins I, Solenberg P, Young M, McHenney M A, Skatrud P L, Rosteck P R., Jr DNA sequence sampling of the Streptococcus pneumoniaegenome to identify novel targets for antibiotic development. Microb Drug Resist. 1998;4:1–9. - PubMed
-
- Black S, et al. Efficacy, safety and immunogenicity of heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2000;19:187–195. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevention of pneumococcal disease: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1997;46(RR-08):1–24. - PubMed
-
- Crain M J, Waltman II W D, Turner J S, Yother J, Talkington D F, McDaniel L S, Gray B M, Briles D E. Pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA) is serologically highly variable and is expressed by all clinically important capsular serotypes of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 1990;58:3293–3299. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

