The imprinted H19 gene is a marker of early recurrence in human bladder carcinoma
- PMID: 11193051
- PMCID: PMC1186987
- DOI: 10.1136/mp.53.6.320
The imprinted H19 gene is a marker of early recurrence in human bladder carcinoma
Abstract
Aims: To investigate the expression of the imprinted oncofetal H19 gene in human bladder carcinoma and to examine the possibility of using it as a tumour marker, similar to other oncofetal gene products.
Methods: In situ hybridisation for H19 RNA was performed on 61 first biopsies of bladder carcinoma from Hadassah Medical Centre in Jerusalem. The intensity of the reaction and the number of tumour cells expressing H19 in each biopsy were evaluated in 56 patients, excluding biopsies with carcinoma in situ. The medical files were searched for demographic data and disease free survival.
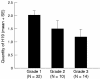
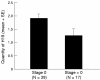
Results: More than 5% of cells expressed H19 in 47 of the 56 (84%) biopsies. There was a decrease in the number of cells expressing H19 with increasing tumour grade (loss of differentiation) (p = 0.03). Disease free survival from the first biopsy to first recurrence was significantly shorter in patients with tumours having a larger fraction of H19 expressing cells, controlling for tumour grade. This was also supported by the selective analysis of tumour recurrence in patients with grade I tumours.
Conclusions: It might be possible to use H19 as a prognostic tumour marker for the early recurrence of bladder cancer. In addition, for the gene therapy of bladder carcinoma that is based on the transcriptional regulatory sequences of H19, the expression of H19 in an individual biopsy could be considered a predictive tumour marker for selecting those patients who would benefit from this form of treatment.
Figures


References
-
- Tilghman SM. The sins of the fathers and the mothers: genomic imprinting in mammalian development. Cell 1999;96:185–93. - PubMed
-
- Bartolomei MS, Zemel S, Tilghman SM. Parental imprinting of the mouse H19 gene. Nature 1991;351:153–5. - PubMed
-
- Rachmilewitz J, Goshen R, Ariel I, et al. Parental imprinting of the human H19 gene. FEBS Lett 1992;309:25–8. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Tycko B. Monoallelic expression of the human H19 gene. Nat Genet 1992;1:40–4. - PubMed
-
- Zemel S, Bartolomei MS, Tilghman SM. Physical linkage of the mammalian imprinted genes H19 and insulin-like growth factor 2. Nat Genet 1992;2:61–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
