Functional anatomy of execution, mental simulation, observation, and verb generation of actions: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 11198101
- PMCID: PMC6872039
- DOI: 10.1002/1097-0193(200101)12:1<1::aid-hbm10>3.0.co;2-v
Functional anatomy of execution, mental simulation, observation, and verb generation of actions: a meta-analysis
Abstract
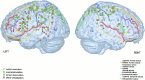
There is a large body of psychological and neuroimaging experiments that have interpreted their findings in favor of a functional equivalence between action generation, action simulation, action verbalization, and perception of action. On the basis of these data, the concept of shared motor representations has been proposed. Indeed several authors have argued that our capacity to understand other people's behavior and to attribute intention or beliefs to others is rooted in a neural, most likely distributed, execution/observation mechanism. Recent neuroimaging studies have explored the neural network engaged during motor execution, simulation, verbalization, and observation. The focus of this metaanalysis is to evaluate in specific detail to what extent the activated foci elicited by these studies overlap.
Figures
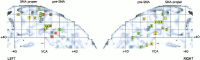
References
-
- Abbruzzese G, Trompetto C, Schieppati M (1996): The excitability of the human motor cortex increases during execution and mental imagination of sequential but not repetitive finger movements. Exp Brain Res 111: 465–472. - PubMed
-
- Allison T, Puce A, McCarthy G (2000): Social perception from visual cues: role of the STS region. TICS 4: 267–278. - PubMed
-
- Amunts K, Schleicher A, Bürgel U, Mohlberg H, Uylings HBM, Zilles K (1999): Broca's region revisited: cytoarchtecture and intersubject variability. J Comp Neurol 412: 319–341. - PubMed
-
- Andersen RA, Snyder LH, Bradley DC, Xing J (1997): Multimodal representation of space in the posterior parietal cortex and its use in planning movements. Annu Rev Neurosci 20: 303–330. - PubMed
-
- Annet J (1996): On knowing how to do things: a theory of motor imagery. Cogn Brain Res 3: 65–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

