Predictive 5-year survivorship model of cystic fibrosis
- PMID: 11207152
- PMCID: PMC2198936
- DOI: 10.1093/aje/153.4.345
Predictive 5-year survivorship model of cystic fibrosis
Abstract
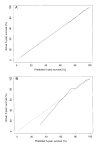
The objective of this study was to create a 5-year survivorship model to identify key clinical features of cystic fibrosis. Such a model could help researchers and clinicians to evaluate therapies, improve the design of prospective studies, monitor practice patterns, counsel individual patients, and determine the best candidates for lung transplantation. The authors used information from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Patient Registry (CFFPR), which has collected longitudinal data on approximately 90% of cystic fibrosis patients diagnosed in the United States since 1986. They developed multivariate logistic regression models by using data on 5,820 patients randomly selected from 11,630 in the CFFPR in 1993. Models were tested for goodness of fit and were validated for the remaining 5,810 patients for 1993. The validated 5-year survivorship model included age, forced expiratory volume in 1 second as a percentage of predicted normal, gender, weight-for-age z score, pancreatic sufficiency, diabetes mellitus, Staphylococcus aureus infection, Burkerholderia cepacia infection, and annual number of acute pulmonary exacerbations. The model provides insights into the complex nature of cystic fibrosis and supplies a rigorous tool for clinical practice and research.
Figures
References
-
- Anderson DH. Cystic fibrosis of the pancreas and its relation to celiac disease. A clinical and pathologic study. Am J Dis Child. 1938;56:344–95.
-
- Farber S. Some organic digestive disturbances in early life. J Michigan Med Sci. 1945;44:587–94.
-
- Cystic Fibrosis Foundation Patient Registry annual data report, 1998. Bethesda, MD; Cystic Fibrosis Foundation: 1999.
-
- Isles A, Maclusky I, Corey M, et al. Pseudomonas cepacia infection in cystic fibrosis: an emerging problem. J Pediatr. 1984;104:206–10. - PubMed
-
- Thomassen MJ, Demko CA, Klinger JD, et al. Pseudomonas cepacia colonization among patients with cystic fibrosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985;131:791–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

