MHC class I-related neonatal Fc receptor for IgG is functionally expressed in monocytes, intestinal macrophages, and dendritic cells
- PMID: 11207281
- PMCID: PMC2827247
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.5.3266
MHC class I-related neonatal Fc receptor for IgG is functionally expressed in monocytes, intestinal macrophages, and dendritic cells
Abstract
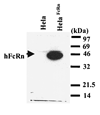
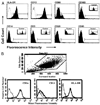
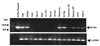
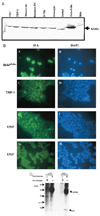
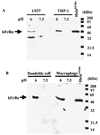
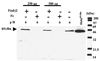
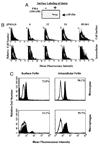
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) for IgG, an MHC class I-related molecule, functions to transport IgG across polarized epithelial cells and protect IgG from degradation. However, little is known about whether FcRn is functionally expressed in immune cells. We show here that FcRn mRNA was identifiable in human monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. FcRn heavy chain was detectable as a 45-kDa protein in monocytic U937 and THP-1 cells and in purified human intestinal macrophages, peripheral blood monocytes, and dendritic cells by Western blot analysis. FcRn colocalized in vivo with macrosialin (CD68) and Ncl-Macro, two macrophage markers, in the lamina propria of human small intestine. The heavy chain of FcRn was associated with the beta(2)-microglobulin (beta(2)m) light chain in U937 and THP-1 cells. FcRn bound human IgG at pH 6.0, but not at pH 7.5. This binding could be inhibited by human IgG Fc, but not Fab. FcRn could be detected on the cell surface of activated, but not resting, THP-1 cells. Furthermore, FcRn was uniformly present intracellularly in all blood monocytes and intestinal macrophages. FcRn was detectable on the cell surface of a significant fraction of monocytes at lower levels and on a small subset of tissue macrophages that expressed high levels of FcRn on the cell surface. These data show that FcRn is functionally expressed and its cellular distribution is regulated in monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, suggesting that it may confer novel IgG binding functions upon these cell types relative to typical Fc gamma Rs: Fc gamma RI, Fc gamma RII, and Fc gamma RIII.
Figures

References
-
- Simister NE, Rees AR. Isolation and characterization of an Fc receptor from neonatal rat small intestine. Eur. J. Immunol. 1985;15:733. - PubMed
-
- Simister NE, Mostov KE. An Fc receptor structurally related to MHC class I antigens. Nature. 1989;337:184. - PubMed
-
- Burmelster WP, Gastinel LN, Simister NE, Blum ML, Bjorkman PJ. Crystal structure at 2.2 Å resolution of the MHC-related neonatal Fc receptor. Nature. 1994;372:336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R37 DK044319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK44319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051362/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK053056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048106/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK51362 , +/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI053056/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034854/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK044319/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK053056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054495/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI041530/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK047322/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK/AI-53056/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

