Increase of chemokine interferon-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) in the serum of patients with autoimmune liver diseases and increase of its mRNA expression in hepatocytes
- PMID: 11207658
- PMCID: PMC1905987
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01391.x
Increase of chemokine interferon-inducible protein-10 (IP-10) in the serum of patients with autoimmune liver diseases and increase of its mRNA expression in hepatocytes
Abstract
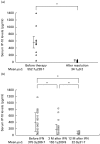
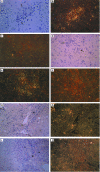
To clarify the role of IP-10 in autoimmune liver diseases, we studied the serum levels of IP-10 in 14 patients with autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), 23 patients with primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC), and 65 patients with chronic viral hepatitis (20 type B and 45 type C). The hepatic expression of IP-10 mRNA and the correlation between the serum levels of IP-10 and clinical parameters were also evaluated. In addition to 20 healthy controls, 16 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were included as an extrahepatic inflammatory disease. The serum level of IP-10 was significantly (P < 0.02) higher in patients with AIH, PBC, and chronic hepatitis B and C than in healthy controls, and it was significantly correlated (P < 0.05) with the serum levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase in patients with AIH, PBC, and chronic hepatitis B and C. The serum level of IP-10 was not elevated in RA patients. After successful treatment of AIH and chronic hepatitis C, the serum level of IP-10 decreased to the same level as in healthy volunteers. As we previously showed in cases with chronic hepatitis B or C, in situ hybridization in both AIH and PBC cases demonstrated the expression of IP-10 mRNA in hepatocytes around focal or lobular necrosis surrounded by infiltrating mononuclear cells, whereas IP-10 mRNA was not expressed in areas around the damaged bile ducts in PBC cases. The present results suggest that IP-10 is specifically produced by hepatocytes in inflammatory areas irrespective of the aetiology of hepatitis, and that IP-10 may help to recruit T cells to the hepatic lesions in autoimmune liver diseases as well as in chronic viral hepatitis.
Figures



References
-
- Scheuer PJ. Viral hepatitis. In: MacSween RNM, Anthony PP, Scheuer PJ, editors. Pathology of the liver. Edinburgh: Chuchill Livingstone; 1987. pp. 202–23.
-
- Dienes HP, Hijtteroth T, Hess G, Meuer SC. Immunoelectron microscopic observations on the inflammatory infiltrates and HLA antigens in hepatitis B and non-A, non-B. Hepatology. 1987;6:1317–25. - PubMed
-
- Bach N, Thung SN, Schaffner F. The histological features of chronic hepatitis C and autoimmune chronic hepatitis: a comparative analysis. Hepatology. 1992;15:572–7. - PubMed
-
- Luster AD. Chemokines—chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:436–45. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

