Increase in tonsillar germinal centre B-1 cell numbers in IgA nephropathy (IgAN) patients and reduced susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 11207662
- PMCID: PMC1905983
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01431.x
Increase in tonsillar germinal centre B-1 cell numbers in IgA nephropathy (IgAN) patients and reduced susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis
Abstract
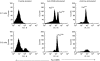
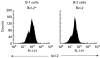
IgAN is a common form of primary glomerulonephritis and also a disease of tonsillar focal infection. The comprehensive mechanism underlying this disease remains to be defined. To better understand its pathogenesis, we investigated tonsillar CD5+ B cells (B-1 cells) with respect to IgA synthesis. Germinal centre (GC) B cells were isolated from the tonsils of IgAN patients and the number of B-1 cells in the GC determined by flow cytometry. GC B-1 and B-2 (CD5- B) cells were purified by cell sorter, the cells were incubated with agonist anti-CD40 MoAb and the ability for antibody production by B-1 and B-2 cells determined by ELISPOT assay. GC B-1 cells and B-2 cells were incubated with agonist anti-Fas MoAb, and apoptosis in GC B-1 cells and B-2 cells was analysed by flow cytometry. Although B-1 cells do not usually take part in the GC reaction, an increase in B-1 cell numbers was observed in the GC of tonsils from IgAN patients. These B-1 cells were likely IgA1 antibody-producing cells, since the prominent IgA subclass in IgAN is generally considered to be IgA1. Although Fas-dependent apoptosis is essential for the elimination of activated B cells, these B-1 cells showed a reduced susceptibility to Fas-mediated apoptosis. It is conceivable that activated B-1 cells may survive in the GC due to impaired apoptosis and thus produce abnormal antibodies. These findings suggest that the immune responses of B-1 cells in the tonsillar GC could thus have an impact on the pathogenesis of IgAN.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Accelerated involution of germinal center in palatine tonsils in IgA nephropathy.PLoS One. 2024 May 6;19(5):e0301853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301853. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38709804 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of CD19(+)CD5(+)B cells and IgA1-positive cells in tonsillar tissues of IgA nephropathy patients.Ren Fail. 2011;33(2):159-63. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2011.552150. Ren Fail. 2011. PMID: 21332337
-
Toll-Like Receptor 9 Stimulation Induces Aberrant Expression of a Proliferation-Inducing Ligand by Tonsillar Germinal Center B Cells in IgA Nephropathy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017 Apr;28(4):1227-1238. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2016050496. Epub 2016 Dec 5. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27920152 Free PMC article.
-
IgA production and tonsillar focal infection in IgA nephropathy.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2012;52(3):161-70. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.52.161. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2012. PMID: 23269075 Review.
-
Relationship between tonsils and IgA nephropathy as well as indications of tonsillectomy.Kidney Int. 2004 Apr;65(4):1135-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00486.x. Kidney Int. 2004. PMID: 15086452 Review.
Cited by
-
A New Vision of IgA Nephropathy: The Missing Link.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 26;21(1):189. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010189. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31888082 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genetics and immunopathogenesis of IgA nephropathy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011 Oct;41(2):198-213. doi: 10.1007/s12016-010-8232-0. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21188648 Review.
-
Effect of tonsillar mononuclear cell supernatants in patients with IgA nephropathy on renal tubular epithelial cells.Inflamm Res. 2013 Jan;62(1):45-52. doi: 10.1007/s00011-012-0549-0. Epub 2012 Sep 25. Inflamm Res. 2013. PMID: 23007808
-
Recent advances in the immunological understanding of association between tonsil and immunoglobulin A nephropathy as a tonsil-induced autoimmune/inflammatory syndrome.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2019 Jun;7(2):86-93. doi: 10.1002/iid3.248. Epub 2019 Apr 7. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2019. PMID: 30957421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Fas/CD95 Receptor Regulates the Death of Autoreactive B Cells and the Selection of Antigen-Specific B Cells.Front Immunol. 2012 Jul 25;3:207. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00207. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22848207 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D'Amico G. Idiopathic IgA mesangial nephropathy. Nephron. 1985;41:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Emancipator SN, Lamm ME. IgA nephropathy: pathogenesis of the most common form of glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1989;60:168–76. - PubMed
-
- Galla JH. IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 1995;47:377–87. - PubMed
-
- Emancipator SN, Rao CS, Amore A, et al. Macromolecular properties that promote mesangial binding and mesangiopathic nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1992;2:S149–58. - PubMed
-
- Yoshioka K, Maki S. Human IgA nephritis: immunocytochemical evidence of a chronic inflammatory proliferative disorder. Histol Histopathol. 1995;10:203–12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

