Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis in rat liver allograft with ongoing rejection by FTY720
- PMID: 11207666
- PMCID: PMC1905974
- DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2001.01434.x
Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis in rat liver allograft with ongoing rejection by FTY720
Abstract
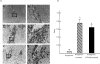
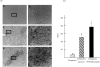
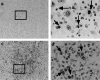
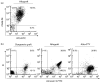
The action mechanism of FTY720, a novel immunosuppressant, is completely different from conventional immunosuppressants. The drug, which triggers apoptosis in murine and human lymphocytes, has a potent immunosuppressive activity to prevent allograft rejection without any severe side-effect. The present study was designed to determine whether FTY720 induces apoptotic cell death in activated lymphocytes infiltrated into liver grafts with ongoing rejection. FTY720 was orally administered at 5 mg/kg to the recipients on day 3 and day 4 after grafting, when the graft rejection was histologically confirmed. The intragraft patterns of IL-2, interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma), perforin, and granzyme B gene expression were detected by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. The treatment reversed ongoing rejection and significantly prolonged recipient survival time compared with the control group. Light microscopic observation of the graft sections stained with the DNA nick-end labelling method showed that the apoptosis in the control allografts was mainly induced in hepatocytes, while that in the FTY720-treated allografts was in infiltrated lymphocytes. The rejection therapy with FTY720 did not alter the expression of IL-2, IFN-gamma, and perforin mRNAs, but slightly decreased granzyme B expression. Our results suggest that FTY720 does not alter the intrinsic lymphocyte function to produce the rejection-related cytokines, but strongly induces apoptotic cell death in the activated lymphocytes. Thus, FTY720 affords new insight into the mechanisms underlying improvements in immunosuppressive treatments.
Figures
References
-
- Fujita T, Yoneta M, Hirose R, et al. Simple compounds, 2-alkyl-2-amino-1,3-propanediols, have potent immunosuppressive activity. Bioorg Med Chem Let. 1995;5:847–53.
-
- Baumann G. Molecular mechanism of immunosuppressive agents. Transplant Proc. 1992;24:4–7. - PubMed
-
- Chiba K, Yanagawa Y, Masubuchi Y, et al. FTY720, a novel immunosuppressant, induces sequestration of circulating mature lymphocytes by acceleration of lymphocyte homing in rats. I. FTY720 selectively decreases the number of circulating mature lymphocytes by acceleration of lymphocyte homing. J Immunol. 1998;160:5037–44. - PubMed
-
- Yanagawa Y, Sugahara K, Kataoka H, et al. FTY720, a novel immunosuppressant, induces sequestration of circulating mature lymphocytes by acceleration of lymphocyte homing in rats. II. FTY720 prolongs skin allograft survival by decreasing T cell infiltration into grafts but not cytokine production in vivo. J Immunol. 1998;160:5493–9. - PubMed
-
- Li XK, Enosawa S, Kakefuda T, et al. FTY720, a novel immunosuppressive agent, enhances upregulation of the cell adhesion molecular ICAM-1 in TNF-alpha treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Transplant Proc. 1997;29:1265–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

