Fatal leukemia in interleukin 15 transgenic mice follows early expansions in natural killer and memory phenotype CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 11208862
- PMCID: PMC2193336
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.193.2.219
Fatal leukemia in interleukin 15 transgenic mice follows early expansions in natural killer and memory phenotype CD8+ T cells
Abstract
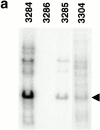
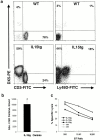
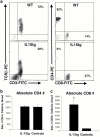
Inflammation likely has a role in the early genesis of certain malignancies. Interleukin (IL)-15, a proinflammatory cytokine and growth factor, is required for lymphocyte homeostasis. Intriguingly, the expression of IL-15 protein is tightly controlled by multiple posttranscriptional mechanisms. Here, we engineered a transgenic mouse to overexpress IL-15 by eliminating these posttranscriptional checkpoints. IL-15 transgenic mice have early expansions in natural killer (NK) and CD8+ T lymphocytes. Later, these mice develop fatal lymphocytic leukemia with a T-NK phenotype. These data provide novel evidence that leukemia, like certain other cancers, can arise as the result of chronic stimulation by a proinflammatory cytokine.
Figures
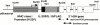














References
-
- Fehniger T.A., Caligiuri M.A. Interleukin 15biology and relevance to human disease. Blood. 2001;97:14–32. - PubMed
-
- Grabstein K.H., Eisenman J., Shanebeck K., Rauch C., Srinivasan S., Fung V., Beers C., Richardson J., Schoenborn M.A., Ahdieh M. Cloning of a T cell growth factor that interacts with the beta chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. Science. 1994;264:965–968. - PubMed
-
- Giri J.G., Kumaki S., Ahdieh M., Friend D.J., Loomis A., Shanebeck K., DuBose R., Cosman D., Park L.S., Anderson D.M. Identification and cloning of a novel IL-15 binding protein that is structurally related to the alpha chain of the IL-2 receptor. EMBO (Eur. Mol. Biol. Organ.) J. 1995;14:3654–3663. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bamford R.N., Grant A.J., Burton J.D., Peters C., Kurys G., Goldman C.K., Brennan J., Roessler E., Waldmann T.A. The interleukin (IL) 2 receptor beta chain is shared by IL-2 and a cytokine, provisionally designated IL-T, that stimulates T-cell proliferation and the induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1994;91:4940–4944. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

