Agents that increase tyrosine phosphorylation activate a non-selective cation current in single rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 11208969
- PMCID: PMC2278409
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0207l.x
Agents that increase tyrosine phosphorylation activate a non-selective cation current in single rabbit portal vein smooth muscle cells
Abstract
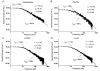
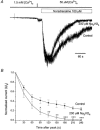
The effects of agents that increase tyrosine phosphorylation were studied with whole-cell recording of membrane currents in single smooth muscle cells from the rabbit portal vein. In K+-free conditions with the chloride equilibrium potential at about -50 mV, intracellular application via the patch pipette of 200 microM sodium orthovanadate (Na3VO4), which inhibits tyrosine phosphatases, activated a "noisy" inward current at a holding potential of -50 mV. Intracellular dialysis with 100 microM (pY)EEI, a peptide activator of the cytosolic tyrosine kinase pp60c-src, and bath application of 5 microM insulin, which activates receptor-coupled tyrosine kinases, also evoked a "noisy" inward current. The current-voltage relationships and the reversal potential (about +10 mV) of the Na3VO4-, pp60c-src- and insulin-induced currents were similar to those of the noradrenaline-evoked non-selective cation current (Icat). The inward currents evoked by noradrenaline, Na3VO4, (pY)EEI and insulin were all greatly potentiated when the bathing calcium concentration was reduced from 1.5 mM to 50 microM. The single channel conductance estimated from spectral density analysis of the whole-cell current was about 20 pS for noradrenaline, Na3VO4, (pY)EEI and insulin. Moreover for all agents the spectra were described by the sum of two Lorentzians with similar corner frequencies. Noradrenaline-evoked Icat was inhibited to a similar degree by the tyrosine kinase inhibitors genistein and tyrphostin 23 and their inactive analogues daidzein and tyrphostin A1, respectively. In the presence of Na3VO4, application of noradrenaline evoked a cation current of similar peak amplitude to control Icat although the rate of decay of Icat was enhanced in the presence of Na3VO4. This study shows that stimulation of both cytosolic and receptor-coupled tyrosine kinases evokes a non-selective cation current and the conductance is similar to that activated by noradrenaline.
Figures

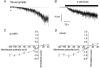


References
-
- Albert AP, Aromolaran AS, Large WA. Tyrosine phosphorylation activates a non-selective cation current in rabbit portal vein myocytes. Journal of Physiology. 1999;521:58.
-
- Di Salvo J, Nelson SR, Kaplan N. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation in smooth muscle: a potential coupling mechanism between receptor activation and intracellular calcium. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine. 1997;214:285–301. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

