Hypertonic enhancement of transmitter release from frog motor nerve terminals: Ca2+ independence and role of integrins
- PMID: 11208972
- PMCID: PMC2278411
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0243l.x
Hypertonic enhancement of transmitter release from frog motor nerve terminals: Ca2+ independence and role of integrins
Abstract
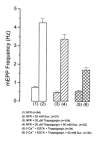
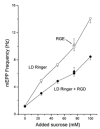
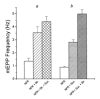
Hyperosmotic solutions cause markedly enhanced spontaneous quantal release of neurotransmitter from many nerve terminals. The mechanism of this enhancement is unknown. We have investigated this phenomenon at the frog neuromuscular junction with the aim of determining the degree to which it resembles the modulation of release by stretch, which has been shown to be mediated by mechanical tension on integrins. The hypertonicity enhancement, like the stretch effect, does not require Ca2+ influx or release from internal stores, although internal release may contribute to the effect. The hypertonicity effect is sharply reduced (but not eliminated) by peptides containing the RGD sequence, which compete with native ligands for integrin bonds. There is co-variance in the magnitude of the stretch and osmotic effects; that is, individual terminals exhibiting a large stretch effect also show strong enhancement by hypertonicity, and vice versa. The stretch and osmotic enhancements also can partially occlude each other. There remain some clear-cut differences between osmotic and stretch forms of modulation: the larger range of enhancement by hypertonic solutions, the relative lack of effect of osmolarity on evoked release, and the reported higher temperature sensitivity of osmotic enhancement. Nevertheless, our data strongly implicate integrins in a significant fraction of the osmotic enhancement, possibly acting via the same mechanism as stretch modulation.
Figures



Comment in
-
Integrins: the missing link.J Physiol. 2001 Jan 15;530(Pt 2):181. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0181l.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11208966 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Kinetics, Ca2+ dependence, and biophysical properties of integrin-mediated mechanical modulation of transmitter release from frog motor nerve terminals.J Neurosci. 1997 Feb 1;17(3):904-16. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.17-03-00904.1997. J Neurosci. 1997. PMID: 8994045 Free PMC article.
-
Integrins and modulation of transmitter release from motor nerve terminals by stretch.Science. 1995 Sep 15;269(5230):1578-80. doi: 10.1126/science.7667637. Science. 1995. PMID: 7667637
-
Regulation of transmitter release by muscle length in frog motor nerve terminals. Dynamics of the effect and the role of integrin-ECM interactions.Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1994;29:383-98. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1994. PMID: 7848723 Review.
-
The role of integrins in the modulation of neurotransmitter release from motor nerve terminals by stretch and hypertonicity.J Neurocytol. 2003 Jun-Sep;32(5-8):489-503. doi: 10.1023/B:NEUR.0000020606.58265.b5. J Neurocytol. 2003. PMID: 15034249 Review.
-
Hypertonicity-induced transmitter release at Drosophila neuromuscular junctions is partly mediated by integrins and cAMP/protein kinase A.J Physiol. 2002 Jan 1;538(Pt 1):103-19. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.012901. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11773320 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrin β1 Promotes Peripheral Entry by Rabies Virus.J Virol. 2020 Jan 6;94(2):e01819-19. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01819-19. Print 2020 Jan 6. J Virol. 2020. PMID: 31666383 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of temperature on vesicular supply and release in autaptic cultures of rat and mouse hippocampal neurons.J Physiol. 2002 Mar 1;539(Pt 2):523-35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2001.013277. J Physiol. 2002. PMID: 11882684 Free PMC article.
-
One month of hyperglycemia alters spectral responses of the zebrafish photopic electroretinogram.Dis Model Mech. 2018 Oct 22;11(10):dmm035220. doi: 10.1242/dmm.035220. Dis Model Mech. 2018. PMID: 30158110 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of integrin-blocking peptide on gadolinium- and hypertonic shrinking-induced neurotransmitter release in rat brain synaptosomes.Neurochem Res. 2008 Jul;33(7):1316-24. doi: 10.1007/s11064-007-9585-5. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Neurochem Res. 2008. PMID: 18270818
-
Studies on integrins in the nervous system.Methods Enzymol. 2007;426:203-21. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(07)26010-0. Methods Enzymol. 2007. PMID: 17697886 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

