Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in disease resistance in tobacco
- PMID: 11209069
- PMCID: PMC14658
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.98.2.741
Activation of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway is involved in disease resistance in tobacco
Abstract
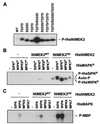
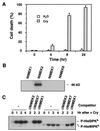
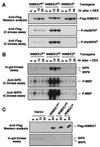
Hypersensitive response (HR), a form of programmed cell death, is frequently associated with plant disease resistance. It has been proposed that mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades regulate HR cell death based on pharmacological studies by using kinase inhibitors. However, direct evidence is lacking. Here, we demonstrate that NtMEK2, a MAPK kinase, is upstream of salicylic acid-induced protein kinase (SIPK) and wounding-induced protein kinase (WIPK), two tobacco MAPKs that are activated by various pathogens or pathogen-derived elicitors. Expression of a constitutively active mutant of NtMEK2 induces HR-like cell death in tobacco, which is preceded by the activation of endogenous SIPK and WIPK. In addition, NtMEK2-SIPK/WIPK cascade appears to control the expression of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl CoA reductase (HMGR) and l-phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), two defense genes encoding key enzymes in the phytoalexin and salicylic acid biosynthesis pathways. These results demonstrate that a plant MAPK cascade controls multiple defense responses against pathogen invasion.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

