synaptotagmin mutants reveal essential functions for the C2B domain in Ca2+-triggered fusion and recycling of synaptic vesicles in vivo
- PMID: 11222632
- PMCID: PMC6762938
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-05-01421.2001
synaptotagmin mutants reveal essential functions for the C2B domain in Ca2+-triggered fusion and recycling of synaptic vesicles in vivo
Abstract
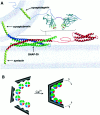
Synaptotagmin has been proposed to function as a Ca(2+) sensor that regulates synaptic vesicle exocytosis, whereas the soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attachment protein receptor (SNARE) complex is thought to form the core of a conserved membrane fusion machine. Little is known concerning the functional relationships between synaptotagmin and SNAREs. Here we report that synaptotagmin can facilitate SNARE complex formation in vitro and that synaptotagmin mutations disrupt SNARE complex formation in vivo. Synaptotagmin oligomers efficiently bind SNARE complexes, whereas Ca(2+) acting via synaptotagmin triggers cross-linking of SNARE complexes into dimers. Mutations in Drosophila that delete the C2B domain of synaptotagmin disrupt clathrin AP-2 binding and endocytosis. In contrast, a mutation that blocks Ca(2+)-triggered conformational changes in C2B and diminishes Ca(2+)-triggered synaptotagmin oligomerization results in a postdocking defect in neurotransmitter release and a decrease in SNARE assembly in vivo. These data suggest that Ca(2+)-driven oligomerization via the C2B domain of synaptotagmin may trigger synaptic vesicle fusion via the assembly and clustering of SNARE complexes.
Figures





References
-
- Bai J, Earles C, Lewis J, Chapman ER. Membrane-embedded synaptotagmin interacts with cis and trans target membranes and assembles into oligomers via a novel mechanism. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:25427–25435. - PubMed
-
- Bark IC, Wilson MC. Human cDNA clones encoding two different isoforms of the nerve terminal protein SNAP-25. Gene. 1994;139:291–292. - PubMed
-
- Bennett MK, Calakos N, Scheller RH. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992;257:255–259. - PubMed
-
- Bollman JH, Sakmann B, Borst JGG. Calcium sensitivity of glutamate release in a Calyx-type terminal. Science. 2000;289:953–957. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
