Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by the interferon-inducible MxA protein
- PMID: 11222692
- PMCID: PMC115893
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.75.6.2684-2691.2001
Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by the interferon-inducible MxA protein
Abstract
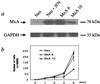
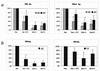
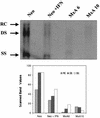
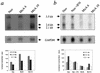
Human MxA is an alpha/beta interferon-inducible intracytoplasmic protein that mediates antiviral activity against several RNA viruses. We had previously shown that overexpression of the hepatitis B virus (HBV) capsid led to selective downregulation of MxA gene expression, suggesting a mechanism by which the virus escapes from the host defense system (O. Rosmorduc, H. Sirma, P. Soussan, E. Gordien, P. Lebon, M. Horisberger, C. Brechot and D. Kremsdorf, J. Gen. Virol. 80:1253-1262, 1999). In the present study, we investigated the antiviral activity of MxA protein against HBV. MxA-expressing HuH7 clones were established and transiently transfected with HBV, and viral replication was then studied. Viral protein secretion was profoundly reduced in MxA-expressing clones by 80% for HBV surface antigen (HBsAg) and 70% for HBV e antigen (HBeAg). The levels of intracytoplasmic HBsAg and HBeAg were reduced by about 80 and 50% in the two MxA-positive clones tested. A nearly complete disappearance of HBV DNA replicative intermediates was observed in MxA-expressing clones. Although the expression of total viral RNAs was not modified, two- to fourfold reductions in HBV cytoplasmic RNAs were found in MxA-expressing clones. This suggests the inhibition of HBV replication at a posttranscriptional level. Indeed, using the well-characterized posttranscriptional regulation element (PRE) reporter system, we were able to demonstrate a marked reduction (three- to eightfold) in the nucleocytoplasmic export of unspliced RNA in MxA-expressing clones. In addition, MxA protein did not interact with HBV nucleocapsid or interfere with HBV nucleocapsid formation. Our results show an antiviral effect of MxA protein on a DNA virus for the first time. MxA protein acts, at least in part, by inhibiting the nucleocytoplasmic export of viral mRNA via the PRE sequence.
Figures
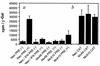
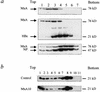
References
-
- Berthillon P, Crance J M, Leveque F, Jouan A, Petit M A, Deloince R, Trepo C. Inhibition of the expression of hepatitis A and B viruses (HAV and HBV) proteins by interferon in a human hepatocarcinoma cell line (PLC/PRF/5) J Hepatol. 1996;25:15–19. - PubMed
-
- Caselmann W H, Meyer M, Scholz S, Hofschneider P H, Koshy R. Type I interferons inhibit hepatitis B virus replication and induce hepatocellular gene expression in cultured liver cells. J Infect Dis. 1992;166:966–971. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

