Exoribonuclease superfamilies: structural analysis and phylogenetic distribution
- PMID: 11222749
- PMCID: PMC56904
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/29.5.1017
Exoribonuclease superfamilies: structural analysis and phylogenetic distribution
Abstract
Exoribonucleases play an important role in all aspects of RNA metabolism. Biochemical and genetic analyses in recent years have identified many new RNases and it is now clear that a single cell can contain multiple enzymes of this class. Here, we analyze the structure and phylogenetic distribution of the known exoribonucleases. Based on extensive sequence analysis and on their catalytic properties, all of the exoribonucleases and their homologs have been grouped into six superfamilies and various subfamilies. We identify common motifs that can be used to characterize newly-discovered exoribonucleases, and based on these motifs we correct some previously misassigned proteins. This analysis may serve as a useful first step for developing a nomenclature for this group of enzymes.
Figures


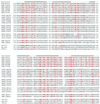

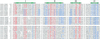

References
-
- Deutscher M.P. and Li,Z. (2000) Exoribonucleases and their multiple roles in RNA metabolism. Prog. Nucleic Acids Res. Mol. Biol., 66, 67–105. - PubMed
-
- Shen V. and Schlessinger,D. (1982) RNase I, II and IV of Escherichia coli. In Boyer,P.D. (ed.), The Enzymes, vol. XV part B. Academic Press, New York, pp. 501–515.
-
- Kasai T., Gupta,R.S. and Schlessinger,D. (1977) Exoribonucleases in wild type Escherichia coli and RNase II-deficient mutants. J. Biol. Chem., 252, 8950–8956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

