The SurA periplasmic PPIase lacking its parvulin domains functions in vivo and has chaperone activity
- PMID: 11226178
- PMCID: PMC140197
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.1.285
The SurA periplasmic PPIase lacking its parvulin domains functions in vivo and has chaperone activity
Abstract
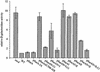
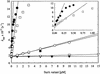
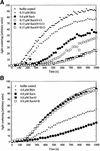
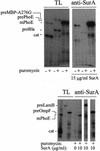
The Escherichia coli periplasmic peptidyl-prolyl isomerase (PPIase) SurA is involved in the maturation of outer membrane porins. SurA consists of a substantial N-terminal region, two iterative parvulin-like domains and a C-terminal tail. Here we show that a variant of SurA lacking both parvulin-like domains exhibits a PPIase-independent chaperone-like activity in vitro and almost completely complements the in vivo function of intact SurA. SurA interacts preferentially (>50-fold) with in vitro synthesized porins over other similarly sized proteins, leading us to suggest that the chaperone-like function of SurA preferentially facilitates maturation of outer membrane proteins.
Figures


References
-
- Bardwell J.C. and Beckwith,J. (1993) The bonds that tie: catalyzed disulfide bond formation. Cell, 74, 769–771. - PubMed
-
- Bardwell J.C., McGovern,K. and Beckwith,J. (1991) Identification of a protein required for disulfide bond formation in vivo. Cell, 67, 581–589. - PubMed
-
- Bosch D., Leunissen,J., Verbakel,J., de Jong,M., van Erp,H. and Tommassen,J. (1986) Periplasmic accumulation of truncated forms of outer-membrane PhoE protein of Escherichia coli K-12. J. Mol. Biol., 189, 449–455. - PubMed
-
- Bothmann H. and Plückthun,A. (1998) Selection for a periplasmic factor improving phage display and functional periplasmic expression. Nature Biotechnol., 16, 376–380. - PubMed
-
- Buchner J., Schmidt,M., Fuchs,M., Jaenicke,R., Rudolph,R., Schmid,F.X. and Kiefhaber,T. (1991) GroE facilitates refolding of citrate synthase by suppressing aggregation. Biochemistry, 30, 1586–1591. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

