Activation and targeting of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by beta-arrestin scaffolds
- PMID: 11226259
- PMCID: PMC30158
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.041604898
Activation and targeting of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by beta-arrestin scaffolds
Abstract
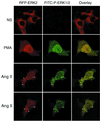
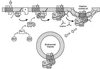
Using both confocal immunofluorescence microscopy and biochemical approaches, we have examined the role of beta-arrestins in the activation and targeting of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (ERK2) following stimulation of angiotensin II type 1a receptors (AT1aR). In HEK-293 cells expressing hemagglutinin-tagged AT1aR, angiotensin stimulation triggered beta-arrestin-2 binding to the receptor and internalization of AT1aR-beta-arrestin complexes. Using red fluorescent protein-tagged ERK2 to track the subcellular distribution of ERK2, we found that angiotensin treatment caused the redistribution of activated ERK2 into endosomal vesicles that also contained AT1aR-beta-arrestin complexes. This targeting of ERK2 reflects the formation of multiprotein complexes containing AT1aR, beta-arrestin-2, and the component kinases of the ERK cascade, cRaf-1, MEK1, and ERK2. Myc-tagged cRaf-1, MEK1, and green fluorescent protein-tagged ERK2 coprecipitated with Flag-tagged beta-arrestin-2 from transfected COS-7 cells. Coprecipitation of cRaf-1 with beta-arrestin-2 was independent of MEK1 and ERK2, whereas the coprecipitation of MEK1 and ERK2 with beta-arrestin-2 was significantly enhanced in the presence of overexpressed cRaf-1, suggesting that binding of cRaf-1 to beta-arrestin facilitates the assembly of a cRaf-1, MEK1, ERK2 complex. The phosphorylation of ERK2 in beta-arrestin complexes was markedly enhanced by coexpression of cRaf-1, and this effect is blocked by expression of a catalytically inactive dominant inhibitory mutant of MEK1. Stimulation with angiotensin increased the binding of both cRaf-1 and ERK2 to beta-arrestin-2, and the association of beta-arrestin-2, cRaf-1, and ERK2 with AT1aR. These data suggest that beta-arrestins function both as scaffolds to enhance cRaf-1 and MEK-dependent activation of ERK2, and as targeting proteins that direct activated ERK to specific subcellular locations.
Figures



References
-
- Hepler J R, Gilman A G. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992;17:383–387. - PubMed
-
- Dhanasekaran N, Heasley L E, Johnson G L. Endocrine Rev. 1995;16:259–270. - PubMed
-
- Gutkind J S. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:1839–1842. - PubMed
-
- Pierce, K. L., Luttrell, L. M. & Lefkowitz, R. J. (2000) Oncogene, in press. - PubMed
-
- Freedman N J, Lefkowitz R J. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1996;51:319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

