Performance characteristics of a quantitative, homogeneous TaqMan RT-PCR test for HCV RNA
- PMID: 11229521
- PMCID: PMC1906908
- DOI: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60632-0
Performance characteristics of a quantitative, homogeneous TaqMan RT-PCR test for HCV RNA
Abstract
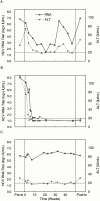
We developed a homogeneous format reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay for quantitating hepatitis C virus (HCV) RNA based on the TaqMan principle, in which signal is generated by cleaving a target-specific probe during amplification. The test uses two probes, one specific for HCV and one specific for an internal control, containing fluorophores with different emission spectra. Titers are calculated in international units (IU)/ml by comparing the HCV signal generated by test samples to that generated by a set of external standards. Endpoint titration experiments demonstrated that samples containing 28 IU/ml give positive results 95% of the time. Based on these data, the limit of detection was set conservatively at 40 IU/ml. All HCV genotypes were amplified with equal efficiency and accurately quantitated: when equal quantities of RNA were tested, each genotype produced virtually identical fluorescent signals. The test exhibited a linear range extending from 64 to 4,180,000 IU/ml and excellent reproducibility, with coefficients of variation ranging from 21.6 to 30.4%, which implies that titers that differ by a factor of twofold (0.3 log10) are statistically significant (P = 0.005). The test did not react with other organisms likely to co-infect patients with hepatitis C and exhibited a specificity of 99% when evaluated on a set of samples from HCV seronegative blood donors. In interferon-treated patients, the patterns of viral load changes revealed by the TaqMan HCV quantitative test distinguished responders from nonresponders and responder-relapsers. These data indicate that the TaqMan quantitative HCV test provides an attractive alternative for measuring HCV viral load and should prove useful for prognosis and for monitoring the efficacy of antiviral treatments.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TaqMan amplification system with an internal positive control for HCV RNA quantitation.J Clin Virol. 2004 Nov;31(3):227-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2004.03.009. J Clin Virol. 2004. PMID: 15465417
-
Clinical performance of the new rRoche COBAS TaqMan HCV Test and High Pure System for extraction, detection and quantitation of HCV RNA in plasma and serum.Antivir Ther. 2006;11(1):95-103. Antivir Ther. 2006. PMID: 16518965
-
Real-time multiplex PCR assay to quantify hepatitis C virus RNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.J Virol Methods. 2006 May;133(2):195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2005.11.007. Epub 2005 Dec 27. J Virol Methods. 2006. PMID: 16384611
-
Comparison of HCV RNA assays for the detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA levels in serum of patients with chronic hepatitis C treated with interferon.J Med Virol. 1997 May;52(1):105-12. J Med Virol. 1997. PMID: 9131466
-
Detection of hepatitis C virus RNA: application to diagnostics and research.Curr Stud Hematol Blood Transfus. 1998;(62):76-101. doi: 10.1159/000060473. Curr Stud Hematol Blood Transfus. 1998. PMID: 9507805 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Performance evaluation of the new Roche cobas AmpliPrep/cobas TaqMan HCV test, version 2.0, for detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA.J Clin Microbiol. 2013 Jan;51(1):238-42. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01729-12. Epub 2012 Nov 14. J Clin Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23152551 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of performance characteristics of three real-time reverse transcription-PCR test systems for detection and quantification of hepatitis C virus.J Clin Microbiol. 2007 Aug;45(8):2529-36. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00058-07. Epub 2007 Jun 13. J Clin Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17567786 Free PMC article.
-
Performance characteristics of a quantitative TaqMan hepatitis C virus RNA analyte-specific reagent.J Clin Microbiol. 2004 Aug;42(8):3739-46. doi: 10.1128/JCM.42.8.3739-3746.2004. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. PMID: 15297524 Free PMC article.
-
Ultracentrifugation of serum samples allows detection of hepatitis C virus RNA in patients with occult hepatitis C.J Virol. 2007 Jul;81(14):7710-5. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02750-06. Epub 2007 May 2. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 17475654 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the COBAS TaqMan HCV test with automated sample processing using the MagNA pure LC instrument.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Jan;43(1):293-8. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.1.293-298.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15634985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Charlton M, Seaberg E, Wiesner R, Everhart J, Zetterman R, Lake J, Detre K, Hoofnagle J: Predictors of patient and graft survival following liver transplantation for hepatitis C. Hepatology 1998, 28:823-830 - PubMed
-
- Fried MW: Clinical applications of hepatitis C virus genotyping and quantitation. Clinics Liver Dis 1997, 1:631-645 - PubMed
-
- Ichijo T, Matsumoto A, Kobayashi M, Furihata K, Tanaka E: Quantitative measurement of HCV RNA in the serum: a comparison of three assays based on different principles. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1997, 12:500-506 - PubMed
-
- : NIH Consensus Statement Online: Management of Hepatitis C. 1997, 15 (http://odp.od.nih.gov/consensus/cons/105/105_statement.htm):1-41 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

