Purification, characterization, and overexpression of flavin reductase involved in dibenzothiophene desulfurization by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1
- PMID: 11229908
- PMCID: PMC92711
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.67.3.1179-1184
Purification, characterization, and overexpression of flavin reductase involved in dibenzothiophene desulfurization by Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1
Abstract
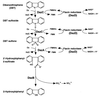
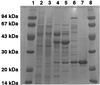
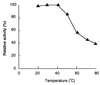
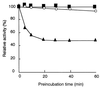
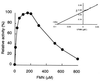
The dibenzothiophene (DBT)-desulfurizing bacterium, Rhodococcus erythropolis D-1, removes sulfur from DBT to form 2-hydroxybiphenyl using four enzymes, DszC, DszA, DszB, and flavin reductase. In this study, we purified and characterized the flavin reductase from R. erythropolis D-1 grown in a medium containing DBT as the sole source of sulfur. It is conceivable that the enzyme is essential for two monooxygenase (DszC and DszA) reactions in vivo. The purified flavin reductase contains no chromogenic cofactors and was found to have a molecular mass of 86 kDa and four identical 22-kDa subunits. The enzyme catalyzed NADH-dependent reduction of flavin mononucleotide (FMN), and the K(m) values for NADH and FMN were 208 and 10.8 microM, respectively. Flavin adenine dinucleotide was a poor substrate, and NADPH was inert. The enzyme did not catalyze reduction of any nitroaromatic compound. The optimal temperature and optimal pH for enzyme activity were 35 degrees C and 6.0, respectively, and the enzyme retained 30% of its activity after heat treatment at 80 degrees C for 30 min. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of the purified flavin reductase was identical to that of DszD of R. erythropolis IGTS8 (K. A. Gray, O. S. Pogrebinsky, G. T. Mrachko, L. Xi, D. J. Monticello, and C. H. Squires, Nat. Biotechnol. 14:1705-1709, 1996). The flavin reductase gene was amplified with primers designed by using dszD of R. erythropolis IGTS8, and the enzyme was overexpressed in Escherichia coli. The specific activity in crude extracts of the overexpressed strain was about 275-fold that of the wild-type strain.
Figures
References
-
- Bradford M M. A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976;72:248–254. - PubMed
-
- Eichhorn E, van der Ploeg J, Leisinger T. Characterization of a two-component alkanesulfonate monooxygenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:26639–26646. - PubMed
-
- Fontecave M, Eliason R, Reichard P. NAD(P)H:flavin oxidoreductase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987;262:12325–12331. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

