GSK-3 kinase Mck1 and calcineurin coordinately mediate Hsl1 down-regulation by Ca2+ in budding yeast
- PMID: 11230131
- PMCID: PMC145470
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.1074
GSK-3 kinase Mck1 and calcineurin coordinately mediate Hsl1 down-regulation by Ca2+ in budding yeast
Abstract
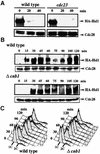
The Ca2+-activated pathways of Saccharomyces cerevisiae induce a delay in the onset of mitosis through the activation of Swe1, a negative regulatory kinase that inhibits the Cdc28-Clb complex. Calcineurin and Mpk1 activate Swe1 at the transcriptional and post-translational level, respectively, and both pathways are essential for the cell cycle delay. Our genetic screening identified the MCK1 gene, which encodes a glycogen synthetase kinase-3 family protein kinase, as a component of the Ca2+ signaling pathway. Genetic analyses indicated that Mck1 functions downstream of the Mpk1 pathway and down-regulates Hsl1, an inhibitory kinase of Swe1. In medium with a high concentration of Ca2+, Hsl1 was delocalized from the bud neck and destabilized in a manner dependent on both calcineurin and Mck1. Calcineurin was required for the dephosphorylation of autophosphorylated Hsl1. The E3 ubiquitin ligase complex SCF(Cdc4), but not the anaphase-promoting complex (APC), was essential for Hsl1 destabilization. The Ca2+-activated pathway may play a role in the rapid inactivation of Hsl1 at the cell cycle stage(s) when APC activity is low.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Dynamic localization of the Swe1 regulator Hsl7 during the Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle.Mol Biol Cell. 2001 Jun;12(6):1645-69. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.6.1645. Mol Biol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11408575 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase stimulation of Ca(2+) signaling is required for survival of endoplasmic reticulum stress in yeast.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Oct;14(10):4296-305. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e03-02-0113. Epub 2003 Jun 27. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 14517337 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc34 and the F-box protein Met30 are required for degradation of the Cdk-inhibitory kinase Swe1.Genes Dev. 1998 Aug 15;12(16):2587-97. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.16.2587. Genes Dev. 1998. PMID: 9716410 Free PMC article.
-
Altered states: programmed proteolysis and the budding yeast cell cycle.Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999 Dec;2(6):610-7. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(99)00030-2. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10607629 Review.
-
Tome-1, wee1, and the onset of mitosis: coupled destruction for timely entry.Mol Cell. 2003 Apr;11(4):845-6. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00149-7. Mol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12718868 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of stress signalling pathways enhances tolerance of fungi to chemical fungicides and antifungal proteins.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014 Jul;71(14):2651-66. doi: 10.1007/s00018-014-1573-8. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24526056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rom2-dependent phosphorylation of Elo2 controls the abundance of very long-chain fatty acids.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 13;290(7):4238-47. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.629279. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25519905 Free PMC article.
-
FaSmi1 Is Essential for the Vegetative Development, Asexual Reproduction, DON Production and Virulence of Fusarium asiaticum.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Nov 11;8(11):1189. doi: 10.3390/jof8111189. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36422010 Free PMC article.
-
Nonapoptotic death of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells that is stimulated by Hsp90 and inhibited by calcineurin and Cmk2 in response to endoplasmic reticulum stresses.Eukaryot Cell. 2008 Dec;7(12):2037-51. doi: 10.1128/EC.00291-08. Epub 2008 Sep 19. Eukaryot Cell. 2008. PMID: 18806210 Free PMC article.
-
Calcineurin promotes adaptation to chronic stress through two distinct mechanisms.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Oct 1;35(10):ar123. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-03-0122. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39083354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amon A., Irniger,S. and Nasmyth,K. (1994) Closing the cell cycle circle in yeast: G2 cyclin proteolysis initiated at mitosis persists until the activation of G1 cyclins in the next cycle.Cell, 77, 1037–1050. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

