The transcription factors MTF-1 and USF1 cooperate to regulate mouse metallothionein-I expression in response to the essential metal zinc in visceral endoderm cells during early development
- PMID: 11230134
- PMCID: PMC145491
- DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.5.1114
The transcription factors MTF-1 and USF1 cooperate to regulate mouse metallothionein-I expression in response to the essential metal zinc in visceral endoderm cells during early development
Abstract
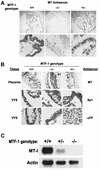
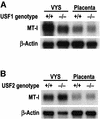
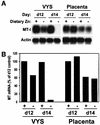
During early development of the mouse embryo, expression of the metallothionein-I (MT-I) gene is heightened specifically in the endoderm cells of the visceral yolk sac. The mechanisms of regulation of this cell-specific pattern of expression of metallothionein-I are unknown. However, it has recently been shown that MTF-1, functioning as a metalloregulatory transcription factor, activates metallothionein genes in response to the essential metal zinc. In contrast with the metallothionein genes, MTF-1 is essential for development; null mutant embryos die due to liver degeneration. We report here that MTF-1 is absolutely essential for upregulation of MT-I gene expression in visceral endoderm cells and that optimal expression also involves interactions of the basic helix-loop-helix upstream stimulatory factor-1 (USF1) with an E-box1-containing sequence at -223 bp in the MT-I promoter. Expression of MT-I in visceral endoderm cells was dependent on maternal dietary zinc. Thus, the essential metal, zinc, apparently provides the signaling ligand that activates cell-specific MT-I expression in visceral endoderm cells.
Figures


References
-
- Andrews G.K. (2000) Regulation of metallothionein gene expression by oxidative stress and metal ions. Biochem. Pharmacol., 59, 95–104. - PubMed
-
- Andrews G.K. and Geiser,J. (1999) Expression of metallothionein-I and -II genes provides a reproductive advantage during maternal dietary zinc deficiency. J. Nutr., 129, 1643–1648. - PubMed
-
- Andrews G.K., Adamson,E.D. and Gedamu,L. (1984) The ontogeny of expression of murine metallothionein: comparison with the α-fetoprotein gene. Dev. Biol., 103, 294–303. - PubMed
-
- Andrews G.K., Gallant,K.R. and Cherian,M.G. (1987a) Regulation of the ontogeny of rat liver metallothionein mRNA by zinc. Eur. J. Biochem., 166, 527–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

