Activation of the Notch-regulated transcription factor CBF1/RBP-Jkappa through the 13SE1A oncoprotein
- PMID: 11230145
- PMCID: PMC312632
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.189301
Activation of the Notch-regulated transcription factor CBF1/RBP-Jkappa through the 13SE1A oncoprotein
Abstract
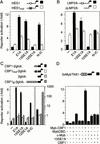
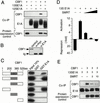
Signaling through the Notch pathway controls cell growth and differentiation in metazoans. Following binding of its ligands, the intracellular part of the cell surface Notch1 receptor (Notch1-IC) is released and translocates to the nucleus, where it alters the function of the DNA-binding transcription factor CBF1/RBP-Jkappa. As a result, CBF1/RBP-Jkappa is converted from a repressor to an activator of gene transcription. Similarly, the Epstein Barr viral oncoprotein EBNA2, which is required for B-cell immortalization, activates genes through CBF1. Moreover, the TAN-1 and int-3 oncogenes represent activated versions of Notch1 and Notch4, respectively. Here, we show that the adenoviral oncoprotein 13S E1A also binds to CBF1/RBP-Jkappa, displaces associated corepressor complexes, and activates CBF1/RBP-Jkappa-dependent gene expression. Our results suggest that the central role of the Notch-CBF1/RBP-Jkappa signaling pathway in cell fate decisions renders it susceptible to pathways of viral replication and oncogenic conversion.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The lytic switch protein of KSHV activates gene expression via functional interaction with RBP-Jkappa (CSL), the target of the Notch signaling pathway.Genes Dev. 2002 Aug 1;16(15):1977-89. doi: 10.1101/gad.996502. Genes Dev. 2002. PMID: 12154127 Free PMC article.
-
Activated Notch1 can transiently substitute for EBNA2 in the maintenance of proliferation of LMP1-expressing immortalized B cells.J Virol. 2001 Mar;75(5):2033-40. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.5.2033-2040.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11160707 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of a novel MHC class I element binding activity from thymus nuclear extracts reveals that thymic RBP-Jkappa/CBF1 binds to NF-kappaB-like elements.J Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;156(12):4672-9. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8648111
-
EBNA2 and Notch signalling in Epstein-Barr virus mediated immortalization of B lymphocytes.Semin Cancer Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):423-34. doi: 10.1006/scbi.2001.0409. Semin Cancer Biol. 2001. PMID: 11669604 Review.
-
HES and HERP families: multiple effectors of the Notch signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Mar;194(3):237-55. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10208. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12548545 Review.
Cited by
-
The anatomical distribution of genetic associations.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Dec 15;43(22):10804-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1262. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 26586807 Free PMC article.
-
Insensitive is a corepressor for Suppressor of Hairless and regulates Notch signalling during neural development.EMBO J. 2011 Jul 15;30(15):3120-33. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.218. EMBO J. 2011. PMID: 21765394 Free PMC article.
-
Developments in Genetics: Better Management of Ovarian Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 5;24(21):15987. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115987. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Manipulation of Epithelial Differentiation by HPV Oncoproteins.Viruses. 2019 Apr 22;11(4):369. doi: 10.3390/v11040369. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31013597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical non-genomic morphogen signaling in anucleate platelets: a critical determinant of prothrombotic function in circulation.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 3;22(1):13. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01448-y. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38172855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Matsuno K, Fortini ME. Notch signaling. Science. 1995;268:225–232. - PubMed
-
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Rand MD, Lake RJ. Notch signaling: Cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science. 1999;284:770–776. - PubMed
-
- Boyer TG, Martin ME, Lees E, Ricciardi RP, Berk AJ. Mammalian Srb/mediator complex is targeted by adenovirus E1A protein. Nature. 1999;399:276–279. - PubMed
-
- Brou C, Logeat F, Lecourtois M, Vandekerckhove J, Kourilsky P, Schweisguth F, Israel A. Inhibition of the DNA-binding activity of Drosophila suppressor of hairless and of its human homolog, KBF2/RBP-Jκ, by direct protein– protein interaction with Drosophila hairless. Genes & Dev. 1994;8:2491–2503. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
