Isolation and characterization of polymorphic DNA from Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 11230401
- PMCID: PMC87847
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.39.3.897-905.2001
Isolation and characterization of polymorphic DNA from Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
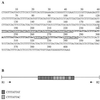
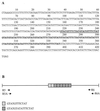
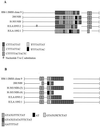
An important gap in our understanding of the epidemiology of amebiasis is what determines the outcome of Entamoeba histolytica infections. To investigate the possible existence of invasive and noninvasive strains as one factor, the ability to differentiate individual isolates of E. histolytica is necessary. Two new loci containing internal repeats, locus 1-2 and locus 5-6, have been isolated. Each contains a single repeat block with two types of related direct repeats arranged in tandem. Southern blot analysis suggests that both loci are multicopy and may themselves be arranged in tandem arrays. Three other previously reported, internally repetitive loci containing at least two repeat blocks each with one or more related repeat units were also investigated. PCR was used to study polymorphism at each of these loci, which was detected to various degrees in each case. Variation was seen in the total number of bands obtained per isolate and their sizes. Nucleotide sequence comparison of loci 1-2 and 5-6 in five axenic isolates revealed differences in the number of repeat units, which correlated with the observed PCR product size variation, and in repeat sequence. Use of multiple loci collectively allowed differentiation of a majority of the 13 isolates studied, and we believe that these loci have the potential to be used as polymorphic molecular markers for investigating the epidemiology of E. histolytica and the potential existence of genetically distinct invasive and noninvasive strains.
Figures
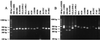




Similar articles
-
Simultaneous differentiation and typing of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Apr;40(4):1271-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1271-1276.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11923344 Free PMC article.
-
SINE polymorphism reveals distinct strains of Entamoeba histolytica from North India.Exp Parasitol. 2017 Apr;175:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Exp Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28131659
-
Remarkable genetic polymorphism among Entamoeba histolytica isolates from a limited geographic area.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Nov;40(11):4081-90. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.11.4081-4090.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 12409379 Free PMC article.
-
[Distinguishing between pathogenic and nonpathogenic isolates of Entamoeba histolytica by polymerase chain reaction].Nihon Rinsho. 1992 Jul;50 Suppl:448-52. Nihon Rinsho. 1992. PMID: 1404938 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Application of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in the epidemiology of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar infections.Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1998 Dec;23(6):413-5. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1998. PMID: 10622639 Review.
Cited by
-
Mutation detection analysis of a region of 16S-like ribosomal RNA gene of Entamoeba histolytica, Entamoeba dispar and Entamoeba moshkovskii.BMC Infect Dis. 2008 Sep 26;8:131. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-8-131. BMC Infect Dis. 2008. PMID: 18822136 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in protein profiles of the isolates of Entamoeba histolytica and E. dispar by surface-enhanced laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (SELDI-TOF MS) ProteinChip assays.Parasitol Res. 2007 Dec;102(1):103-10. doi: 10.1007/s00436-007-0736-z. Epub 2007 Sep 11. Parasitol Res. 2007. PMID: 17846790
-
Comparative genomic hybridizations of Entamoeba strains reveal unique genetic fingerprints that correlate with virulence.Eukaryot Cell. 2005 Mar;4(3):504-15. doi: 10.1128/EC.4.3.504-515.2005. Eukaryot Cell. 2005. PMID: 15755913 Free PMC article.
-
Coding and noncoding genomic regions of Entamoeba histolytica have significantly different rates of sequence polymorphisms: implications for epidemiological studies.J Clin Microbiol. 2005 Sep;43(9):4815-9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.43.9.4815-4819.2005. J Clin Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16145147 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous differentiation and typing of Entamoeba histolytica and Entamoeba dispar.J Clin Microbiol. 2002 Apr;40(4):1271-6. doi: 10.1128/JCM.40.4.1271-1276.2002. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11923344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson T J C, Su X Z, Bockarie M, Lagog M, Day K P. Twelve microsatellite markers for characterisation of Plasmodium falciparum from finger-prick blood samples. Parasitology. 1999;119:113–125. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. WHO/PAHO/UNESCO report. A consultation with experts on amoebiasis. Epidemiol Bull PAHO. 1997;18:13–14. - PubMed
-
- Azam A, Paul J, Sehgal D, Prasad J, Bhattacharya S, Bhattacharya A. Identification of novel genes from Entamoeba histolytica by expressed sequence tag analysis. Gene. 1996;181:113–116. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharya S, Bhattacharya A, Diamond L S. Entamoeba histolytica extrachromosomal circular ribosomal DNA: analysis of clonal variation in a hypervariable region. Exp Parasitol. 1992;74:200–204. - PubMed
-
- Blanc D S, Sargeaunt P G. Entamoeba histolytica zymodemes: exhibition of γ and δ bands only of glucose phosphate isomerase and phosphoglucomutase may be influenced by starch content in the medium. Exp Parasitol. 1991;72:87–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

