Identification of a contaminating Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain with a transposition of an IS6110 insertion element resulting in an altered spoligotype
- PMID: 11230432
- PMCID: PMC87878
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.37.3.1092-1096.2001
Identification of a contaminating Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain with a transposition of an IS6110 insertion element resulting in an altered spoligotype
Abstract
Molecular fingerprinting with the IS6110 insertion sequence is useful for tracking transmission of Mycobacterium tuberculosis within a population or confirming specimen contamination in the laboratory or through instrumentation. Secondary typing with other molecular methods yields additional information as to the relatedness of strains with similar IS6110 fingerprints. Isolated, relatively rare, random events within the M. tuberculosis genome alter molecular fingerprinting patterns with any of the methods; therefore, strains which are different by two or more typing methods are usually not considered to be closely related. In this report, we describe two strains of M. tuberculosis, obtained from the same bronchoscope 2 days apart, that demonstrated unique molecular fingerprinting patterns by two different typing methods. They were closely linked through the bronchoscope by a traditional epidemiologic investigation. Genetic analysis of the two strains revealed that a single event, the transposition of an IS6110 insertion sequence in one of the strains, accounted for both the differences in the IS6110 pattern and the apparent deletion of a spacer in the spoligotype. This finding shows that a single event can change the molecular fingerprint of a strain in two different molecular typing systems, and thus, molecular typing cannot be the only means used to track transmission of this organism through a population. Traditional epidemiologic techniques are a necessary complement to molecular fingerprinting so that radical changes within the fingerprint pattern can be identified.
Figures
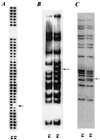
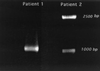

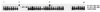
Comment in
-
IS6110 insertions in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: predominantly into coding regions.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Sep;39(9):3423-4. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.9.3423-3424.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11558473 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Genetic mutations occur gradually in in vivo populations of Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria.J Clin Microbiol. 2001 Oct;39(10):3814. doi: 10.1128/JCM.39.10.3814.2001. J Clin Microbiol. 2001. PMID: 11599522 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Agerton T, Valway S, Gore B, Pozsik C, Plikaytis B, Woodley C, Onorato I. Transmission of a highly drug-resistant strain (strain W1) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Community outbreak and nosocomial transmission via a contaminated bronchoscope. JAMA. 1997;278:1073–1077. - PubMed
-
- Akamatsu T, Tabata K, Hironaga M, Uyeda M. Evaluation of the efficacy of a 3.2% glutaraldehyde product for disinfection of fibreoptic endoscopes with an automatic machine. J Hosp Infect. 1997;35:47–57. - PubMed
-
- Aranaz A, Liébana E, Mateos A, Dominguez L, Vidal D, Domingo M, Gonzolez O, Rodriguez-Ferri E F, Bunschoten A E, Van Embden J D, Cousins D. Spacer oligonucleotide typing of Mycobacterium bovis strains from cattle and other animals: a tool for studying epidemiology of tuberculosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1996;34:2734–2740. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

