Expression and permeation properties of the K(+) channel Kir7.1 in the retinal pigment epithelium
- PMID: 11230507
- PMCID: PMC2278466
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0329i.x
Expression and permeation properties of the K(+) channel Kir7.1 in the retinal pigment epithelium
Abstract
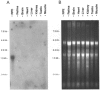
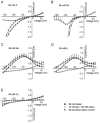
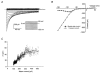
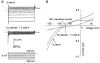
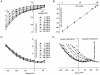
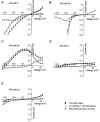
Bovine Kir7.1 clones were obtained from a retinal pigment epithelium (RPE)-subtracted cDNA library. Human RPE cDNA library screening resulted in clones encoding full-length human Kir7.1. Northern blot analysis indicated that bovine Kir7.1 is highly expressed in the RPE. Human Kir7.1 channels were expressed in Xenopus oocytes and studied using the two-electrode voltage-clamp technique. The macroscopic Kir7.1 conductance exhibited mild inward rectification and an inverse dependence on extracellular K+ concentration ([K+]o). The selectivity sequence based on permeability ratios was K+ (1.0) approximately Rb+ (0.89) > Cs+ (0.013) > Na+ (0.003) approximately Li+ (0.001) and the sequence based on conductance ratios was Rb+ (9.5) >> K+ (1.0) > Na+ (0.458) > Cs+ (0.331) > Li+ (0.139). Non-stationary noise analysis of Rb+ currents in cell-attached patches yielded a unitary conductance for Kir7.1 of approximately 2 pS. In whole-cell recordings from freshly isolated bovine RPE cells, the predominant current was a mild inwardly rectifying K+ current that exhibited an inverse dependence of conductance on [K+]o. The selectivity sequence based on permeability ratios was K+ (1.0) approximately Rb+ (0.89) > Cs+ (0.021) > Na+ (0.003) approximately Li+ (0.002) and the sequence based on conductance ratios was Rb+ (8.9) >> K+ (1.0) > Na+ (0.59) > Cs+ (0.23) > Li+ (0.08). In cell-attached recordings with Rb+ in the pipette, inwardly rectifying currents were observed in nine of 12 patches of RPE apical membrane but in only one of 13 basolateral membrane patches. Non-stationary noise analysis of Rb+ currents in cell-attached apical membrane patches yielded a unitary conductance for RPE Kir of approximately 2 pS. On the basis of this molecular and electrophysiological evidence, we conclude that Kir7.1 channel subunits comprise the K+ conductance of the RPE apical membrane.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Expression and localization of the inwardly rectifying potassium channel Kir7.1 in native bovine retinal pigment epithelium.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003 Jul;44(7):3178-85. doi: 10.1167/iovs.02-1189. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003. PMID: 12824269
-
Expression and functional properties of unique inward rectifier K+ channel Kir7.1 in the porcine iris and retinal pigment epithelium.Curr Eye Res. 2003 Nov;27(5):279-87. doi: 10.1076/ceyr.27.5.279.17226. Curr Eye Res. 2003. PMID: 14562164
-
Functional Kir7.1 channels localized at the root of apical processes in rat retinal pigment epithelium.J Physiol. 2001 Feb 15;531(Pt 1):27-36. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0027j.x. J Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11179389 Free PMC article.
-
Properties of the inwardly rectifying K+ conductance in the toad retinal pigment epithelium.J Physiol. 1994 Apr 1;476(1):41-53. J Physiol. 1994. PMID: 8046634 Free PMC article.
-
Focus on Kir7.1: physiology and channelopathy.Channels (Austin). 2014;8(6):488-95. doi: 10.4161/19336950.2014.959809. Channels (Austin). 2014. PMID: 25558901 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mutations in KCNJ13 cause autosomal-dominant snowflake vitreoretinal degeneration.Am J Hum Genet. 2008 Jan;82(1):174-80. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2007.08.002. Am J Hum Genet. 2008. PMID: 18179896 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Kir channels in bovine retinal pigment epithelial cells by phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Oct;297(4):C1001-11. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00250.2009. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19641096 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Electroretinogram after Kir7.1 Channel Suppression Suggests Role in Retinal Electrophysiology.Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 6;7(1):10651. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-11034-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28878288 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of inwardly rectifying potassium channel subunits in native human retinal pigment epithelium.Exp Eye Res. 2008 Sep;87(3):176-83. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2008.05.010. Epub 2008 May 28. Exp Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18653180 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of Kir7.1 and a novel Kir7.1 splice variant in native human retinal pigment epithelium.Exp Eye Res. 2008 Jan;86(1):81-91. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2007.09.011. Epub 2007 Oct 2. Exp Eye Res. 2008. PMID: 18035352 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K. Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. New York: John Wiley & Sons; 1996.
-
- Chang JT, Esumi N, Moore K, Li Y, Zhang S, Chew C, Goodman B, AmirRattner A, Moody S, Stetten G, Campochiaro PA, Zack DJ. Cloning and characterization of a secreted frizzled-related protein that is expressed by the retinal pigment epithelium. Human Molecular Genetics. 1999;8:575–583. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

