Alexander disease: diagnosis with MR imaging
- PMID: 11237983
- PMCID: PMC7976831
Alexander disease: diagnosis with MR imaging
Abstract
Background and purpose: To date, the demonstration of Rosenthal fibers on brain biopsy or autopsy specimens is considered a prerequisite for a definitive diagnosis of Alexander disease. We initiated a multiinstitutional survey of MR abnormalities in both presumed and confirmed cases of Alexander disease to assess the possibility of an MR-based diagnosis.
Methods: MR imaging studies in three patients with an autopsy-based diagnosis of Alexander disease were analyzed to define MR criteria for the diagnosis. These criteria were then applied to 217 children with leukoencephalopathy of unknown origin.
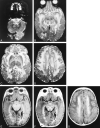
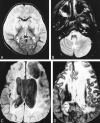
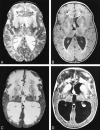
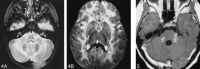
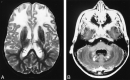
Results: Five MR imaging criteria were defined: extensive cerebral white matter changes with frontal predominance, a periventricular rim with high signal on T1-weighted images and low signal on T2-weighted images, abnormalities of basal ganglia and thalami, brain stem abnormalities, and contrast enhancement of particular gray and white matter structures. Four of the five criteria had to be met for an MR imaging-based diagnosis. In a retrospective analysis of the MR studies of the 217 patients, 19 were found who fulfilled these criteria. No other essentially new MR abnormalities were found in these patients. In four of the 19 patients, subsequent histologic confirmation was obtained. The clinical symptomatology was the same in the patients with and without histologic confirmation and correlated well with the MR abnormalities. MR abnormalities were in close agreement with the known histopathologic findings of Alexander disease.
Conclusion: The defined criteria are sufficient for an in vivo MR imaging diagnosis of Alexander disease; only in atypical cases is a brain biopsy still necessary for a definitive diagnosis.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander WS. Progressive fibrinoid degeneration of fibrillary astrocytes associated with mental retardation in a hydrocephalic child. Brain 1949;72:373-381 - PubMed
-
- Crome L. Megalencephaly associated with hyaline neuropathy. Brain 1953;76:215-228 - PubMed
-
- Wohlwill FJ, Bernstein J, Yakovlev PI. Dysmyelogenic leukodystrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1959;18:359-383 - PubMed
-
- Holland IM, Kendall BE. Computed tomography in Alexander's disease. Neuroradiology 1980;20:103-106 - PubMed
-
- Towfighi J, Young R, Sassani J, Ramer J, Horoupian DS. Alexander's disease: further light- and electron-microscopic observations. Acta Neuropathol 1983;61:36-42 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
