Intrachoroidal neovascularization in transgenic mice overexpressing vascular endothelial growth factor in the retinal pigment epithelium
- PMID: 11238064
- PMCID: PMC1850362
- DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64063-1
Intrachoroidal neovascularization in transgenic mice overexpressing vascular endothelial growth factor in the retinal pigment epithelium
Abstract
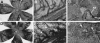
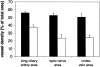
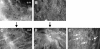
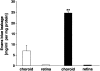
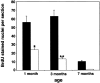
Choroidal neovascularization in age-related macular degeneration is a frequent and poorly treatable cause of vision loss in elderly Caucasians. This choroidal neovascularization has been associated with the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). In current animal models choroidal neovascularization is induced by subretinal injection of growth factors or vectors encoding growth factors such as VEGF, or by disruption of the Bruch's membrane/retinal pigment epithelium complex with laser treatment. We wished to establish a transgenic murine model of age-related macular degeneration, in which the overexpression of VEGF by the retinal pigment epithelium induces choroidal neovascularization. A construct consisting of a tissue-specific murine retinal pigment epithelium promoter (RPE(65) promoter) coupled to murine VEGF(164) cDNA with a rabbit beta-globin-3' UTR was introduced into the genome of albino mice. Transgene mRNA was expressed in the retinal pigment epithelium at all ages peaking at 4 months. The expression of VEGF protein was increased in both the retinal pigment epithelium and choroid. An increase of intravascular adherent leukocytes and vessel leakage was observed. Histopathology revealed intrachoroidal neovascularization that did not penetrate through an intact Bruch's membrane. These results support the hypothesis that additional insults to the integrity of Bruch's membrane are required to induce growth of choroidal vessels into the subretinal space as seen in age-related macular degeneration. This model may be useful to screen for inhibitors of choroidal vessel growth.
Figures

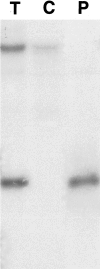
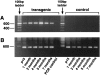
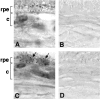
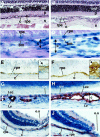
References
-
- Adamis AP, Shima DT, Yeo KT, Yeo TK, Brown LF, Berse B, D’Amore PA, Folkman J: Synthesis and secretion of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor by human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1993, 193:631-638 - PubMed
-
- Lutty G, Grunwald J, Majji AB, Uyama M, Yoneya S: Changes in choriocapillaris and retinal pigment epithelium in age-related macular degeneration. Mol Vis 1999, 5:35. - PubMed
-
- Amin R, Puklin JE, Frank RN: Growth factor localization in choroidal neovascular membranes of age-related macular degeneration. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1994, 35:3178-3188 - PubMed
-
- Frank RN, Amin RH, Eliott D, Puklin JE, Abrams GW: Basic fibroblast growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor are present in epiretinal and choroidal neovascular membranes. Am J Ophthalmol 1996, 122:393-403 - PubMed
-
- Kvanta A, Algvere PV, Berglin L, Seregard S: Subfoveal fibrovascular membranes in age-related macular degeneration express vascular endothelial growth factor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1996, 37:1929-1934 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

