Differentiation of two bovine lentiviruses by a monoclonal antibody on the basis of epitope specificity
- PMID: 11238209
- PMCID: PMC96050
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.2.283-287.2001
Differentiation of two bovine lentiviruses by a monoclonal antibody on the basis of epitope specificity
Erratum in
- Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2001 May;8(3):670
Abstract
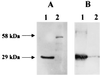
Bovine immunodeficiency virus (BIV) and Jembrana disease virus (JDV) are bovine lentiviruses that are closely related genetically. A recombinant fusion protein containing the capsid protein of BIV expressed in Escherichia coli was used to immunize mice and produce monoclonal antibodies. Six hybridomas specific for BIV capsid protein were identified, and one antibody, designated 10H1, was characterized further. Competitive binding assays were performed to analyze the topography of antigenic determinants by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and demonstrated the existence of at least three distinct antigenic determinants on capsid protein. The monoclonal antibody reacted specifically with both BIV capsid and the recombinant fusion protein in Western immunoblot analyses. However, it did not react with the recombinant capsid fusion protein of JDV, indicating that BIV contains at least one unique epitope in the capsid protein that is absent in JDV. Further mapping of the epitope by chemical cleavage analysis identified that the epitope is located at the 6.4-kDa N terminus of the 29-kDa capsid protein. This monoclonal antibody assay will be valuable for distinguishing the two closely related lentiviruses by Western blotting.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Serological evidence of an Australian bovine lentivirus.Vet Microbiol. 1999 Aug 16;68(1-2):171-7. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1135(99)00073-5. Vet Microbiol. 1999. PMID: 10501174
-
Recombinant Jembrana disease virus gag proteins identify several different antigenic domains but do not facilitate serological differentiation of JDV and nonpathogenic bovine lentiviruses.J Virol Methods. 2005 Mar;124(1-2):135-42. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2004.11.015. Epub 2004 Dec 29. J Virol Methods. 2005. PMID: 15664061
-
Recombinant Jembrana disease virus proteins as antigens for the detection of antibody to bovine lentiviruses.J Virol Methods. 1998 Sep;74(1):39-46. doi: 10.1016/s0166-0934(98)00066-4. J Virol Methods. 1998. PMID: 9763127
-
Recent advances in the understanding of Jembrana disease.Vet Microbiol. 1995 Sep;46(1-3):249-55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(95)00089-s. Vet Microbiol. 1995. PMID: 8545963 Review.
-
[The bovine immunodeficiency virus: 1990-1992 update].Vet Res. 1993;24(2):179-87. Vet Res. 1993. PMID: 8393724 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Bovine immunodeficiency virus: a lentiviral infection.Indian J Virol. 2013 Dec;24(3):332-41. doi: 10.1007/s13337-013-0165-9. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Indian J Virol. 2013. PMID: 24426295 Free PMC article.
-
Unique epitope of bovine immunodeficiency virus gag protein spans the cleavage site between p16(MA) and p2L.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002 Nov;9(6):1277-81. doi: 10.1128/cdli.9.6.1277-1281.2002. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12414761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amborski G F, Lo J L, Seger C L. Serological detection of multiple retroviral infection in cattle: bovine leukemia virus, bovine syncytial virus and bovine visna virus. Vet Microbiol. 1989;20:247–253. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson B, Liu Z Q, Wood C. Use of bacterial trpE fusion vectors to express and characterize the bovine immunodeficiency like virus core protein. J Virol Methods. 1992;36:35–39. - PubMed
-
- Burkala E J, Narayani I, Hartaningsih N, Kertayadnya G, Berryman D, Wilcox G E. Recombinant Jembrana disease virus proteins as antigens for the detection of antibody to bovine lentiviruses. J Virol Methods. 1998;74:39–46. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

