N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine inhibits both gamma interferon- and interleukin-10-induced expression of FcgammaRI on human monocytes
- PMID: 11238229
- PMCID: PMC96070
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.2.402-408.2001
N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine inhibits both gamma interferon- and interleukin-10-induced expression of FcgammaRI on human monocytes
Abstract
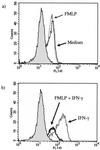
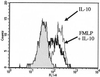
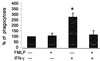
Three different classes of receptors for the Fc portion of immunoglobulin G (FcgammaRs), FcgammaRI, FcgammaRII, and FcgammaRIII, have been identified on human leukocytes. One of them, FcgammaRI, is a high-affinity receptor capable of induction of functions that include phagocytosis, respiratory burst, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), and secretion of cytokines. This receptor is expressed on mononuclear phagocytes, and this expression is regulated by cytokines and hormones such as gamma interferon (IFN-gamma), IFN-beta, interleukin-10 (IL-10), and glucocorticoids. We have recently demonstrated that the chemotactic peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) is capable of inducing a time-dependent downregulation of both FcgammaRIIIB and FcgammaRII in human neutrophils, altering FcgammaR-dependent functions. Considering the biological relevance of the regulation of FcgammaRI, we investigated the effect of FMLP on the overexpression of FcgammaRI induced by both IFN-gamma and IL-10 on human monocytes. We demonstrate that FMLP significantly abrogated IFN-gamma- and IL-10-induced FcgammaRI expression, although its basal level of expression was not altered. However, other IFN-gamma-mediated effects such as the overexpression of the major histocompatibility complex class II antigens and the enhancement of lipopolysaccharide-induced secretion of tumor necrosis factor alpha were not affected by FMLP treatment. The formyl peptide completely inhibited the IFN-gamma- and IL-10-induced enhancement of ADCC and phagocytosis carried out by adherent cells. The inhibitory effect of FMLP on FcgammaRI upregulation could exert an important regulatory effect during the evolution of bacterial infections.
Figures
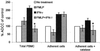
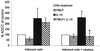
Similar articles
-
Monocytes and neutrophils from tuberculosis patients are insensitive to anti-inflammatory effects triggered by the prototypic formyl peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP).Clin Exp Immunol. 2003 Aug;133(2):267-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02212.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12869034 Free PMC article.
-
The formyl peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine downregulates the expression of FcgammaRs in interferon-gamma-activated monocytes/macrophages in vitro and in vivo.Scand J Immunol. 2003 Mar;57(3):221-8. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3083.2003.01219.x. Scand J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12641650
-
Hypothesis: an alternative pathway for the regulation of inflammation.Medicina (B Aires). 2004;64(3):235-9. Medicina (B Aires). 2004. PMID: 15239538
-
Human neutrophil Fc gamma RIIIB and formyl peptide receptors are functionally linked during formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine-induced chemotaxis.J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):989-97. J Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1321856
-
The main functions and structural modifications of tripeptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP) as a chemotactic factor.Pharmazie. 2008 Nov;63(11):779-83. Pharmazie. 2008. PMID: 19069235 Review.
Cited by
-
Monocytes and neutrophils from tuberculosis patients are insensitive to anti-inflammatory effects triggered by the prototypic formyl peptide N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP).Clin Exp Immunol. 2003 Aug;133(2):267-74. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.2003.02212.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12869034 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate biomarkers for discrimination between infection and disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis.J Mol Med (Berl). 2007 Jun;85(6):613-21. doi: 10.1007/s00109-007-0157-6. Epub 2007 Feb 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007. PMID: 17318616
-
N-Formyl-Methionyl-Leucyl-Phenylalanine Plays a Neuroprotective and Anticonvulsant Role in Status Epilepticus Model.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Nov;43(8):4231-4244. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01410-z. Epub 2023 Sep 24. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37742326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alves-Rosa M F, Vulcano M, Minucci F, di Gianni P, Isturiz M A. Inhibition of FcγR-dependent functions by N-formylmethionylleucylphenylalanine in human neutrophils. Clin Exp Immunol. 1997;83:147–155. - PubMed
-
- Alves-Rosa M F, Vulcano M, Beigier M, Breyer M, Isturiz M A. The down-regulation of FcγRII and FcγRIIB by N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) depends on secretory events in human neutrophils. Immunol Lett. 1999;70:119–126. - PubMed
-
- Arend W P, Ammons J T, Kotzin B L. Lipopolysaccharide and interleukin-1 inhibit interferon induced Fc receptor expression on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1987;139:1873–1879. - PubMed
-
- Bach E A, Auguet M, Schreiber R D. The IFN-γ receptor: a paradigm for cytokine receptor signalling. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:563–591. - PubMed
-
- Ball E D, McDermott J, Griffin J D, Davey F R, Davis R, Bloomfield C D. Expression of the three myeloid cell-associated immunoglobulin G Fc receptors defined by murine monoclonal antibodies on normal bone marrow and acute leukemia cells. Blood. 1989;73:1951–1956. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

