Enzyme immunoassay detection of antigen-specific immunoglobulin g antibodies in longitudinal serum samples from patients with cryptosporidiosis
- PMID: 11238231
- PMCID: PMC96072
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.2.415-423.2001
Enzyme immunoassay detection of antigen-specific immunoglobulin g antibodies in longitudinal serum samples from patients with cryptosporidiosis
Abstract
Cryptosporidium parvum is a protozoan parasite that causes diarrheal illness in a wide range of mammalian hosts, including humans. Characteristic serum immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody responses to antigens in the 27- and 17-kDa size ranges have been shown to develop after infection, and several enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and Western blot assay formats have been used to measure these IgG levels in human serum. Using a collection of serial samples from laboratory-confirmed cryptosporidiosis patients, we compared the results obtained by using two new ELISAs with those obtained with two different Western blot assays. When assayed with the large-format Western blot, 97% of the 67 patients had a demonstrable antibody response on at least one occasion. The Cp23 ELISA correctly identified 93% of the samples that had a 27-kDa response by Western blot and 100% of the negative samples. The Triton antigen ELISA detected 77% of the samples that had a 17-kDa response by Western blot and 88% of the negative samples. The sensitivity of the Triton antigen assay was higher for samples collected between 16 and 92 days after the onset of symptoms (96%). The minigel-format Western blot did not compare favorably with the large-format blot for the detection of antibodies to the 27-kDa antigen (71% sensitivity). A half-life of about 12 weeks was estimated for antibodies to both the 27- and 17-kDa antigens. We believe the Cp23 and Triton antigen ELISAs will be useful in epidemiologic studies of the prevalence of Cryptosporidium infection in the population.
Figures
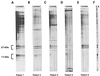


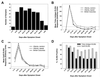
Comment in
-
Quality assurance considerations in cryptosporidium antibody tests.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003 Jan;10(1):193; author reply 193-4. doi: 10.1128/cdli.10.1.193-194.2003. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12522064 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Campbell I, Tzipori A S, Hutchinson G, Angus K W. Effect of disinfectants on survival of Cryptosporidium oocysts. Vet Rec. 1982;111:414–415. - PubMed
-
- DuPont H L, Chappel C L, Sterling C R, Okhuysen P C, Rose J B, Jakubowski W. The infectivity of Cryptosporidium parvum in healthy volunteers. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:855–859. - PubMed
-
- Dworkin M S, Goldman D P, Wells T G, Kobayashi J M, Herwaldt B L. Cryptosporidiosis in Washington State: an outbreak associated with well water. J Infect Dis. 1996;174:1372–1376. - PubMed
-
- Flanigan T, Whalen C, Turneer J, Soave R, Toerner J, Havlir D, Kotler D. Cryptosporidium infection and CD4 counts. Ann Intern Med. 1992;116:840–842. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

