Dose-dependent circulating immunoglobulin A antibody-secreting cell and serum antibody responses in Swedish volunteers to an oral inactivated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine
- PMID: 11238232
- PMCID: PMC96073
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.2.424-428.2001
Dose-dependent circulating immunoglobulin A antibody-secreting cell and serum antibody responses in Swedish volunteers to an oral inactivated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine
Abstract
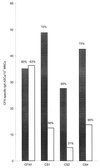
The immunogenicity of different preparations of an oral inactivated enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) vaccine was evaluated in Swedish volunteers previously unexposed to ETEC infection. The vaccine preparations consisted of recombinant cholera toxin B subunit (CTB) and various amounts of formalin-killed whole bacteria expressing the most prevalent colonization factor antigens (CFAs). Significant immunoglobulin A (IgA) antibody-secreting cell (ASC) responses against CTB and the various CFA components were seen in a majority of volunteers after two doses of ETEC vaccine independent of the vaccine lot given. The IgA ASC responses against CTB were significantly higher after the second than after the first immunization, whereas the CFA-specific IgA ASC responses were almost comparable after the first and second doses of ETEC vaccine. Two immunizations with one-third of a full dose of CFA-ETEC bacteria induced lower frequencies of IgA ASC responses against all the different CFAs than two full vaccine doses, i.e., 63 versus 80% for CFA/I, 56 versus 70% for CS1, 31 versus 65% for CS2, and 56 versus 75% for CS4. The proportion of vaccinees responding with rises in the titer of serum IgA antibody against the various CFA antigens was also lower after immunization with the reduced dose of CFA-ETEC bacteria. These findings suggest that measurements of circulating IgA ASCs can be used not only for qualitative but also for quantitative assessments of the immunogenicity of individual fimbrial antigens in various preparations of ETEC vaccine.
Figures
References
-
- Åhrén C, Wennerås C, Holmgren J, Svennerholm A-M. Intestinal antibody response after oral immunization with a prototype cholera B subunit-colonization factor antigen enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli vaccine. Vaccine. 1993;11:929–934. - PubMed
-
- Black R E. The epidemiology of diarrheal disease: implications for control by vaccines. Vaccine. 1993;11:100–106. - PubMed
-
- Clemens J D, Sack D A, Harris J R, Chakraborty J, Neogy P K, Stanton B, Huda N, Khan M U, Kay B A, Khan M R, Ansaruzzaman M, Yunus M, Rao M R, Svennerholm A-M, Holmgren J. Cross-protection by B subunit-whole cell cholera vaccine against diarrhea associated with heat-labile toxin-producing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli: results of a large-scale field trial. J Infect Dis. 1988;158:372–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

