Suppression of endotoxin- and staphylococcal exotoxin-induced cytokines and chemokines by a phospholipase C inhibitor in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 11238238
- PMCID: PMC96079
- DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.8.2.449-453.2001
Suppression of endotoxin- and staphylococcal exotoxin-induced cytokines and chemokines by a phospholipase C inhibitor in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
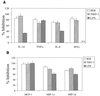
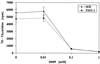
Excessive release of proinflammatory cytokines from cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or staphylococcal exotoxin (SE) mediates the pathophysiologic manifestations of septic shock. Tricyclodecan-9-yl (D609), an inhibitor of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C, suppressed LPS- or SE-induced cytokines and chemokines in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These data suggest a potential role for D609 in the treatment of septic shock.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Caspase inhibitors attenuate superantigen-induced inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and T-cell proliferation.Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004 May;11(3):621-4. doi: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.621-624.2004. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15138192 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of mouse endotoxin shock by inhibition of phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 May;285(2):800-4. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998. PMID: 9580629
-
Lipopolysaccharide activated phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase C and induced IL-8 and MCP-1 production in vascular endothelial cells.J Cell Physiol. 2011 Jun;226(6):1694-701. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22500. J Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21413027
-
An overview on immune system and migraine.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2007 Jul-Aug;11(4):245-8. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17876959 Review.
-
Detection of human cytokine-secreting cells in distinct anatomical compartments.Immunol Rev. 1991 Feb;119:5-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1991.tb00575.x. Immunol Rev. 1991. PMID: 1904397 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Update on staphylococcal superantigen-induced signaling pathways and therapeutic interventions.Toxins (Basel). 2013 Sep 24;5(9):1629-54. doi: 10.3390/toxins5091629. Toxins (Basel). 2013. PMID: 24064719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of endotoxin, TNF-alpha, and IL-6 in inducing the state of growth hormone insensitivity.World J Gastroenterol. 2002 Jun;8(3):531-6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v8.i3.531. World J Gastroenterol. 2002. PMID: 12046086 Free PMC article.
-
Trauma induced heterotopic ossification patient serum alters mitogen activated protein kinase signaling in adipose stem cells.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):7035-7044. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26504. Epub 2018 Apr 10. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29377109 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic down-modulators of staphylococcal superantigen-induced inflammation and toxic shock.Toxins (Basel). 2010 Aug;2(8):1963-83. doi: 10.3390/toxins2081963. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Toxins (Basel). 2010. PMID: 22069668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR, a pathway less recognized for staphylococcal superantigen-induced toxicity.Toxins (Basel). 2012 Nov 15;4(11):1343-66. doi: 10.3390/toxins4111343. Toxins (Basel). 2012. PMID: 23202320 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abraham E, Glauser M P, Butler T, et al. P55 tumor necrosis factor receptor fusion protein in the treatment of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock: a randomized controlled multicenter clinical trial. JAMA. 1997;277:1531–1538. - PubMed
-
- Bergdoll M S, Schlievert P M. Toxic shock syndrome toxin. Lancet. 1984;ii:691.
-
- Calandra T, Baumgartner J D, Grau G E, et al. Prognostic values of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin, interleukin-1, interferon-alpha, and interferon-gamma in the serum of patients with septic shock. J Infect Dis. 1990;161:982–987. - PubMed
-
- Chatila T, Geha R S. Signal transduction of microbial superantigens via MHC class II molecules. Immunol Rev. 1993;131:43–59. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

